RUNX2 (NM_004348) Human Recombinant Protein
CAT#: TP760214
Recombinant protein of human runt-related transcription factor 2 (RUNX2), transcript variant 3, full length, with N-terminal HIS tag, expressed in E.Coli, 50ug
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Species | Human |
| Expression Host | E. coli |
| Expression cDNA Clone or AA Sequence |
A DNA sequence encoding human full-length RUNX2
|
| Tag | N-His |
| Predicted MW | 54.9 kDa |
| Concentration | >0.05 µg/µL as determined by microplate BCA method |
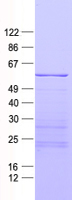
| Purity | > 80% as determined by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie blue staining |
| Buffer | 25 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.0, 150 mM NaCl, 1% sarkosyl, 10% glycerol |
| Note | For testing in cell culture applications, please filter before use. Note that you may experience some loss of protein during the filtration process. |
| Storage | Store at -80°C. |
| Stability | Stable for 12 months from the date of receipt of the product under proper storage and handling conditions. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Reference Data | |
| RefSeq | NP_004339 |
| Locus ID | 860 |
| UniProt ID | Q13950 |
| Cytogenetics | 6p21.1 |
| Refseq Size | 5720 |
| Refseq ORF | 1521 |
| Synonyms | AML3; CBFA1; CCD; CCD1; OSF-2; OSF2; PEA2aA; PEBP2A1; PEBP2A2; PEBP2aA; PEBP2aA1 |
| Summary | This gene is a member of the RUNX family of transcription factors and encodes a nuclear protein with an Runt DNA-binding domain. This protein is essential for osteoblastic differentiation and skeletal morphogenesis and acts as a scaffold for nucleic acids and regulatory factors involved in skeletal gene expression. The protein can bind DNA both as a monomer or, with more affinity, as a subunit of a heterodimeric complex. Two regions of potential trinucleotide repeat expansions are present in the N-terminal region of the encoded protein, and these and other mutations in this gene have been associated with the bone development disorder cleidocranial dysplasia (CCD). Transcript variants that encode different protein isoforms result from the use of alternate promoters as well as alternate splicing. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2016] |
| Protein Families | Druggable Genome, Transcription Factors |
Documents
| FAQs |
| SDS |
Resources
Recombinant Protein Resources |
Other Versions
| SKU | Description | Size | Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| LC400402 | RUNX2 HEK293T cell transient overexpression lysate (as WB positive control) |
USD 206.00 |
|
| LC401387 | RUNX2 HEK293T cell transient overexpression lysate (as WB positive control) |
USD 206.00 |
|
| LY400402 | Transient overexpression lysate of runt-related transcription factor 2 (RUNX2), transcript variant 1 |
USD 665.00 |
|
| LY401387 | Transient overexpression lysate of runt-related transcription factor 2 (RUNX2), transcript variant 3 |
USD 665.00 |
{0} Product Review(s)
Be the first one to submit a review






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China