Immunology

Immunology is the study of the immune system that includes a complex network of cells such as T cells, B cells, and macrophages and organs like the spleen and lymph nodes. Each cell and organ is characterized by the presence of a specific marker. OriGene offers a range of tools to characterize these markers including validated cDNA clones, purified recombinant proteins, recombinant antibodies and more.
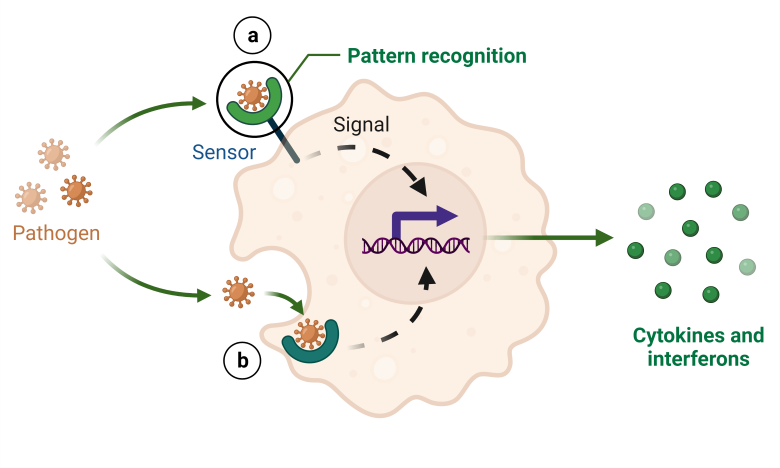
Innate immunity
Innate immune response is a multi-step process that includes the detection of pathogens by pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) and activation of innate immune response involving the production of cytokines and chemokines that recruit and activate the immune cells, such as phagocytes and natural killer (NK) cells, to the site of infection.
Key markers (view all)
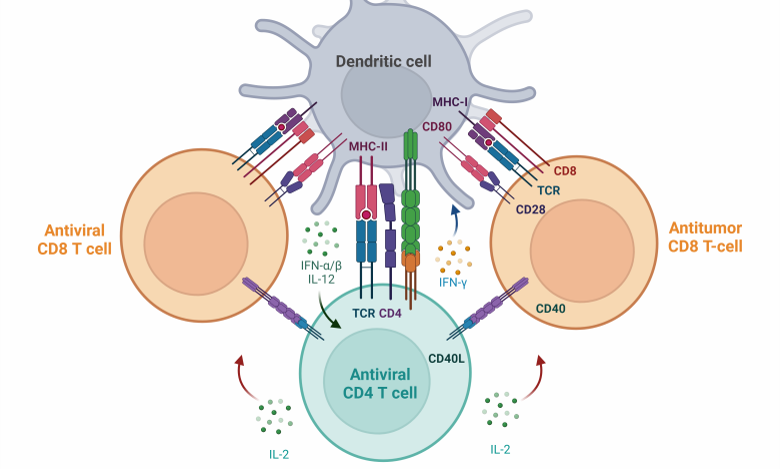
Adaptive immunity
Adaptive immunity is a highly specific and tailored response to an invading pathogen. The status of adaptive immune response can be assessed by testing for the presence of pathogen specific antibodies, memory T cells, cytokines, and T cell receptor (TCR) diversity.
Key markers (view all)
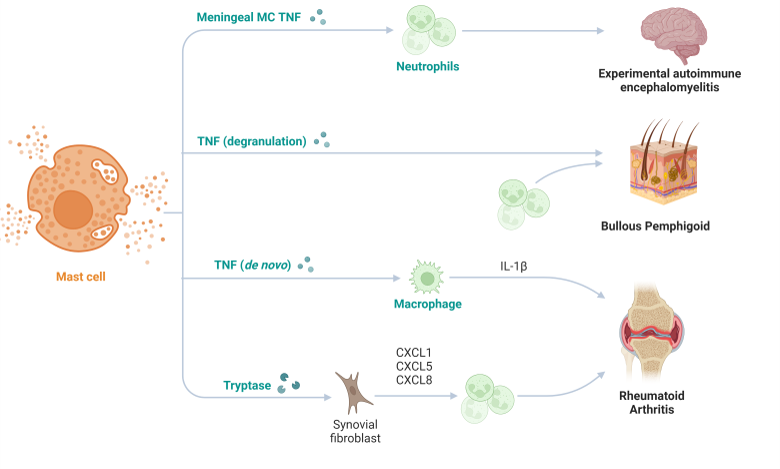
Autoimmunity
Adaptive immunity is a highly specific and tailored response to an invading pathogen. The status of adaptive immune response can be assessed by testing for the presence of pathogen specific antibodies, memory T cells, cytokines, and T cell receptor (TCR) diversity.
Key markers (view all)
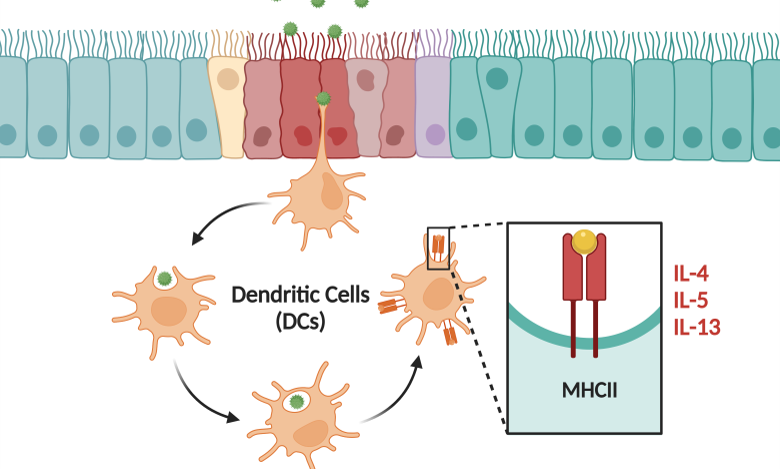
Allergies
Allergic diseases are immune system disorders that occur when the body's immune system becomes hypersensitive to certain substances, allergens. Allergens trigger the release of chemicals called histamines in the body, leading to various symptoms. Different types of allergic diseases include hay fever, asthma, eczema, and conjunctivitis. Treatment of allergic diseases may include medication to immunotherapy to desensitize the body.
Key markers (view all)
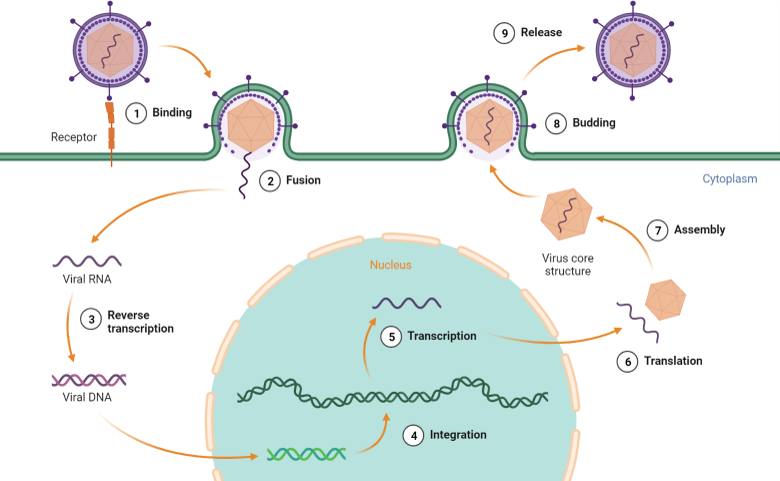
Infectious diseases
Infectious diseases are illnesses caused by pathogens such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites. When immunity is impaired, uncontrolled infection leads to disease. Some infections, such as the flu or the common cold, are caused by viruses that can reproduce and spread quickly within the body. Other infections, such as tuberculosis or HIV/AIDS, can persist in the body for long periods and require more sustained immune responses to control.
Key markers (view all)
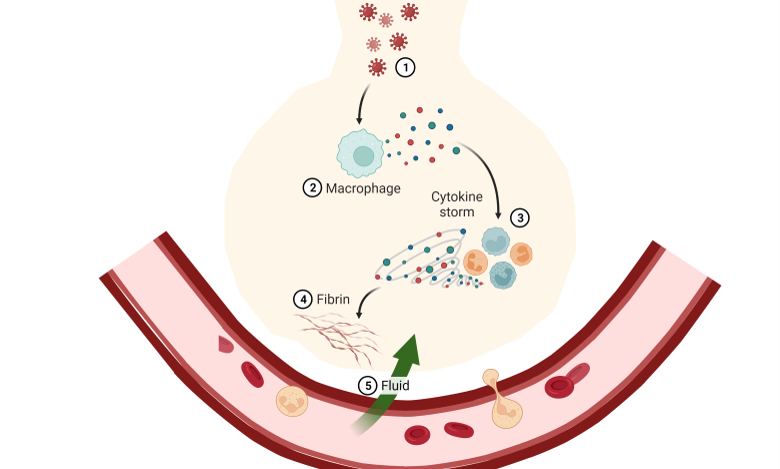
Cytokines
Cytokines are small proteins produced and released by cells in the immune system. They are involved in cell signaling and play a crucial role in the immune response. Cytokines can act on the cells that produce them (autocrine action), on nearby cells (paracrine action), or cells in other parts of the body (endocrine action). Cytokines play a vital role in the immune response and can have beneficial and detrimental effects on the body. Dysregulation of cytokine production can lead to autoimmune disorders and inflammatory diseases.
Key markers (view all)
Hot Topics
- BioSimilars
- KRAS
- Stem Cells
- Liver Diseases
- HSD17B
- HSD17B13
- Pancreatic Cancer
- Colorectal Cancer
- ROR
- LZTFL1
- CD47
- MAGE Family
- CD1C
- Spatial Proteomics
- LGR5
- Antibody Panels
- HTT
- MAGE-A4
Neuroscience
- Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
- Huntington's Disease
- Parkinson's Disease
- Alzheimer’s Disease
- Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI)
- Astrocyte Markers
Oncology
- Cancer Biomarkers
- CD Markers
- Exosomes
- Immuno Oncology
- Extracellular Matrices
- Breast Cancer
- Cervical Cancer
- Lung Cancer
- Leukemia
- IL-6 Signaling Pathway
Virus
Immunology
- Macrophage Markers
- B cell Lineage
- Immune Checkpoint
- Regulatory T cells
- Tumor-Associated Macrophages
- Cancer Testis Antigen
- TH17
- Dendritic Cells
- Allergies / Allergic Diseases
- Cytokines
