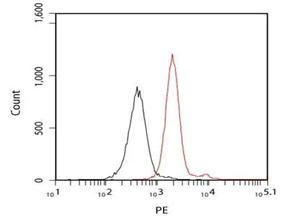
Breast Cancer
Protein Biomarkers for Breast Cancer Research
Integrating functional proteomic analysis with genomic risk scores has a significant potential to augment treatment strategies in breast cancer. With IHC4 (ER, PR, HER2, Ki-67) well established, here is a list of very promising protein biomarkers with a potential for clinical adoption.
Tools for analyzing the IHC4:
Tools for analyzing the IHC4:
Breast cancer is a heterogeneous disease characterized by high genomic instability. Copy number variations, somatic mutations and chromosomal rearrangements are some of the frequently seen genetic alterations. Breast cancer is classified into 4 major subtypes: Luminal A, Luminal B, Triple negative, HER2 enriched [1][2]. It is determined by the tumor stage, tumor grade, status of the hormone receptors (PR, ER) and the mutation status of HER2.
Genes in breast cancer:
Genes that convey moderate risk:
MicroRNA in Breast Cancer [3]
microRNAs are small non-coding RNA molecules that play a significant role in regulation of gene expression via RNA silencing and post-transcriptional regulation pathways. In breast cancer, differential expression of miRNA plays a critical role in regulating the invasion process by influencing cytoskeletal structure, cell-cell adhesion junctions, cancer cell-ECM interaction, tumor microenvironment, EMT transition and cancer stem cell abilities. Understanding miRNA’s role in breast cancer will enable a better management of breast cancer metastasis.
Human miRNAs in breast cancer:
Refer to the table below for a list of all microRNAs involved in breast cancer
References
- Associations between cancer predisposition testing panel genes and breast cancer, Couch et al, JAMA, 2017
- Identification of six key miRNAs associated with breast cancer through screening large-scale microarray data, Liang et al, Oncol Lett. 2018
- MicroRNAs contribute to breast cancer invasiveness, Fridichova et al., Cell, 2019