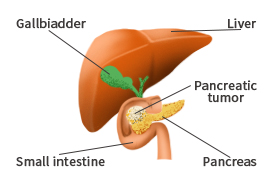
Pancreatic Cancer
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), also called pancreatic cancer is predicted to become the 2nd frequent cause of cancer related death by 2030 (1,2). Recent studies have found that the tumor microenvironment characterized by ample stromal cells and a complex extracellular matrix composition are the main contributing factors. Genetic mutations such as point mutations, insertions, deletions, amplifications, translocations, fusions and inversions are frequently seen in PDACS.
Genes mutated in PDAC
KRAS TP53 CDKN2A SMAD4 RNF43 ARID1A BRCA1 GNAS BRCA2 TGFBR2OriGene has the largest collection Mutant ORF Clones that are conveniently cloned in mammalian expression and dual tagging vector and is available as transfection ready DNA. In addition, here are other tools for analyzing genes associated with PDAC.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China