KRAS
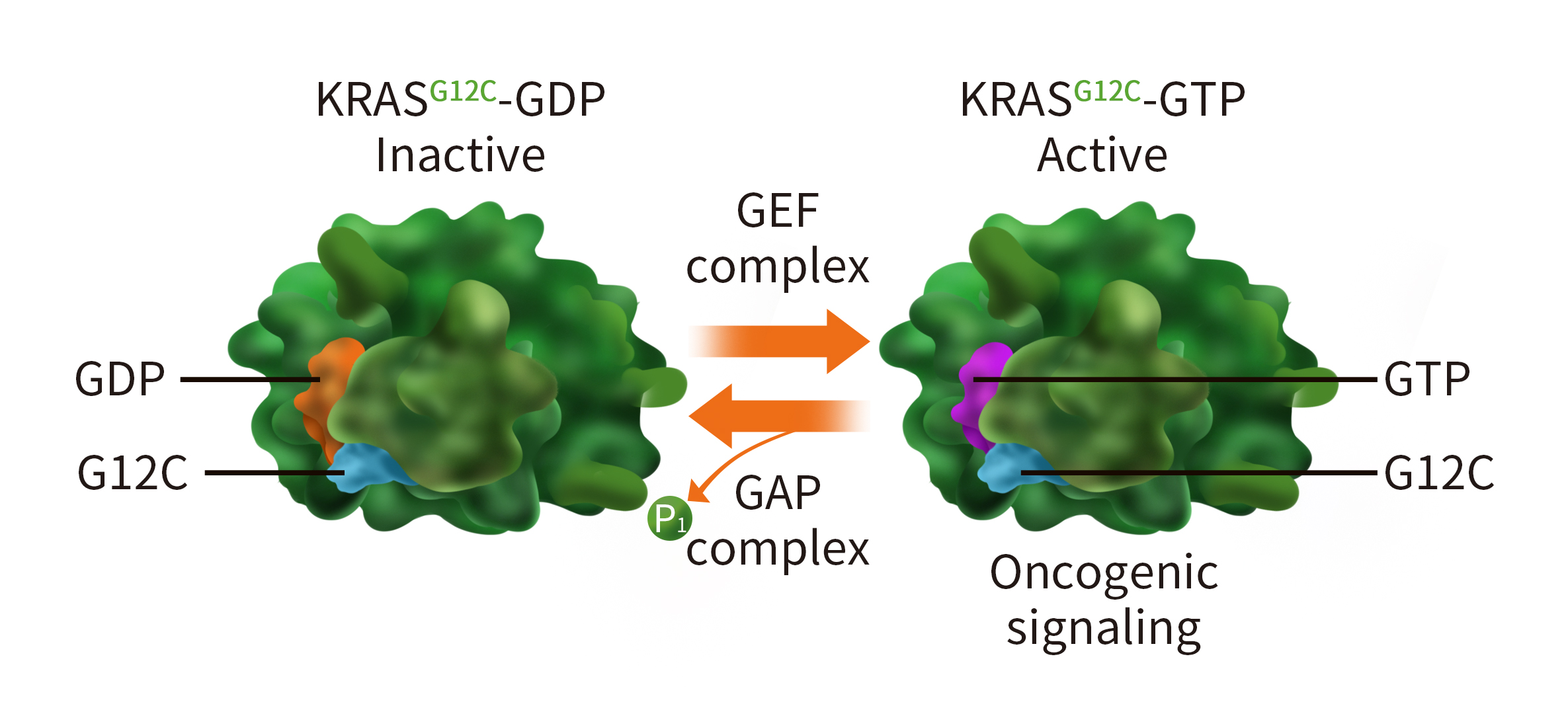
GTPase KRas (KRAS) is a transducer protein that plays a critical role in regulating a range of cellular processes including cell proliferation. Like all GTPases proteins, KRAS is active only when it is bound to GTP. Hydrolysis of GTP to GDP returns it to an its inactive state. In its active state, it binds and activates its effector proteins such as RAF-Kinases, PI3K and RalGDS and activates several cellular signaling pathways including mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway.
How Wild-type KRAS works?

Tools for analyzing KRAS
Mutant KRAS
Mutations in the Ras proteins leads to defective switching mechanism resulting in an overactive RAS, a major driver in human cancer. Of the three, KRAS is the predominantly mutant isoform (85%) followed by NRas (11%) and HRas (4%). While mutations are frequently seen at positions G12, G13 and Q61.3; most oncogenic properties are attributed to G12 and G13 mutations. Among the three isoforms, mutations in position 12 is most predominantly seen in KRAS.
How does mutant KRAS works?
OriGene has the largest collection KRAS Mutant ORF Clones that are conveniently cloned in mammalian expression and dual tagging vector and is available as transfection ready DNA.
ORF Clones of G12 mutant variants
Other KRAS Mutants
KRAS mutant protein expression service
We express these G12 mutant strain in HEK293T cells, verify target protein expression by western blot and supply to you either as cell lysate (OEL controls) or cell pellets embedded in FFPE blocks (CytoSections). Contact our sales team for details at sales@origene.com.
Lung cancer tissue controls
References
- Pantsar T. The current understanding of KRAS protein structure and dynamics. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2019;18:189-198. Published 2019 Dec 26. doi:10.1016/j.csbj.2019.12.004 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6965201
- Villalobos et al, 2017 Feb; 31(1): 13–29. DOI: 10.1016/j.hoc.2016.08.006
- Pakkala et al., 2018 Aug 9;3(15):e120858. DOI:10.1172/jci.insight.120858
- Goebel et al.; 2020 July 1 11 (7): DOI:10.1039/d0md00096e
- Ryan et al., 2018 Nov 15 (11): DOI:10.1038/s41571-018-0105-0
- Image reference: https://www.amgenoncology.com/targets/kras.html
- Mármol I, Sánchez-de-Diego C, Pradilla Dieste A, Cerrada E, Rodriguez Yoldi MJ. Colorectal Carcinoma: A General Overview and Future Perspectives in Colorectal Cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Jan 19;18(1):197. DOI: 10.3390/ijms18010197. PMID: 28106826; PMCID: PMC5297828https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28106826/
