ROR (Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Like Orphan Receptors)
The ROR (Receptor Orphan Receptor) are receptor tyrosine kinases that interact with WNT proteins and play a critical role in development. The ROR family contains two members: ROR1 and ROR2. Both are single-pass transmembrane receptors that bind WNT ligands and activate the downstream β-catenin-independent signaling.
Recent studies have shown that RORs are generally not expressed/expressed at low levels in adult tissues but un-uniformly expressed in multiple cancers as shown in the table.
ROR1 in cancer
ROR1 overexpression is not only seen in hematological malignancies but also in solid tumors such as cancers of the breast, pancreas, and lung.
ROR1 specific tools:
cDNAclones Lentiviral
Particles Antibodies
Recombinant
Proteins OEL controls
(verified WB control) CytoSections
(verified IHC control)
ROR2 in cancer
The role ROR2 in hematological cancers is unclear and needs more studies. Even in other cancers, ROR2 expression is heterogeneous. Its expression is often described as a positive prognostic factor for solid tumors. One of the challenges with ROR2 is that many commercial antibodies display non-specific binding leading to disputable results.
ROR2 specific tools:
cDNAclones Lentiviral
Particles Antibodies
Recombinant
Proteins OEL controls
(verified WB control) CytoSections
(verified IHC control)
References:
- Menck, K.; Heinrichs, S.; Baden, C.; Bleckmann, A. The WNT/ROR Pathway in Cancer: From Signaling to Therapeutic Intervention. Cells 2021, 10, 142.
- Klein, U.; Tu, Y.; Stolovitzky, G.A.; Mattioli, M.; Cattoretti, G.; Husson, H.; Freedman, A.; Inghirami, G.; Cro, L.; Baldini, L.; et al. Gene Expression Profiling of B Cell Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Reveals a Homogeneous Phenotype Related to Memory B Cells. J. Exp. Med. 2001, 194, 1625–1638.
- Rosenwald, A.; Alizadeh, A.A.; Widhopf, G.; Simon, R.; Davis, R.E.; Yu, X.; Yang, L.; Pickeral, O.K.; Rassenti, L.Z.; Powell, J.; et al. Relation of Gene Expression Phenotype to Immunoglobulin Mutation Genotype in B Cell Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. J. Exp. Med. 2001, 194, 1639–1648.
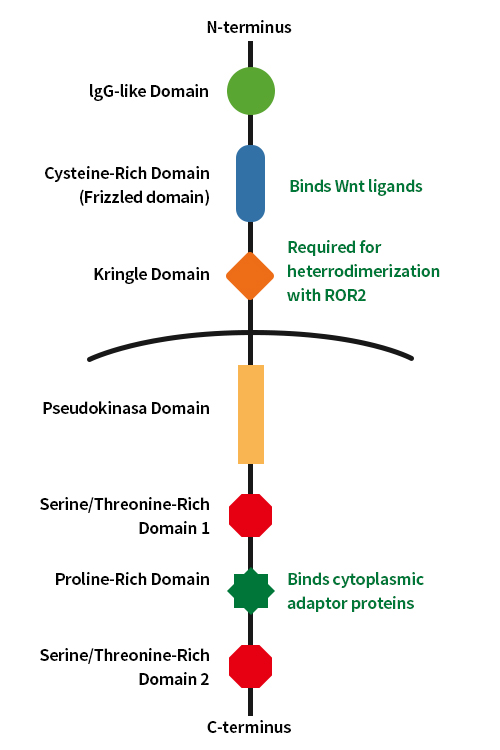 ROR pseudokinase structure
ROR pseudokinase structure
RORs expression in cancer
| Cancer Entity | Expression |
|---|---|
| acute lymphocytic leukemia | ROR1+ |
| chronic lymphocytic leukemia | ROR1+ |
| diffuse large B cell lymphoma | ROR1+ |
| follicular lymphoma | ROR1+ |
| mantle cell lymphoma | ROR1+ |
| marginal zone lymphoma | ROR1+ |
| multiple myeloma | ROR2+ |
| breast cancer | ROR1+ ROR2+ |
| cervical cancer | ROR1+ ROR2+ |
| colorectal cancer | ROR1+ ROR2+/- |
| endometrial cancer | ROR1+ ROR2+ |
| gastric cancer | ROR1+ ROR2- |
| glioblastoma | ROR2+ |
| lung cancer | ROR1+ ROR2+ |
| melanoma | ROR1+ |
| mesothelioma | ROR1+ ROR2+ |
| ovarian cancer | ROR1+ ROR2+/- |
| sarcoma | ROR2+ |
| pancreatic cancer | ROR1+ ROR2+ |
| prostate cancer | ROR2- |






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China