TPM4 (NM_003290) Human Recombinant Protein
CAT#: TP301133
Recombinant protein of human tropomyosin 4 (TPM4), transcript variant 2, 20 µg
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Species | Human |
| Expression Host | HEK293T |
| Expression cDNA Clone or AA Sequence |
>RC201133 protein sequence
Red=Cloning site Green=Tags(s) MAGLNSLEAVKRKIQALQQQADEAEDRAQGLQRELDGERERREKAEGDVAALNRRIQLFEEELDRAQERL ATALQKLEEAEKAADESERGMKVIENRAMKDEEKMEIQEMQLKEAKHIAEEADRKYEEVARKLVILEGEL ERAEERAEVSELKCGDLEEELKNVTNNLKSLEAASEKYSEKEDKYEEEIKLLSDKLKEAETRAEFAERTV AKLEKTIDDLEEKLAQAKEENVGLHQTLDQTLNELNCI TRTRPLEQKLISEEDLAANDILDYKDDDDKV |
| Tag | C-Myc/DDK |
| Predicted MW | 28.3 kDa |
| Concentration | >0.05 µg/µL as determined by microplate BCA method |
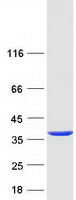
| Purity | > 80% as determined by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie blue staining |
| Buffer | 25 mM Tris-HCl, 100 mM glycine, pH 7.3, 10% glycerol |
| Preparation | Recombinant protein was captured through anti-DDK affinity column followed by conventional chromatography steps. |
| Note | For testing in cell culture applications, please filter before use. Note that you may experience some loss of protein during the filtration process. |
| Storage | Store at -80°C. |
| Stability | Stable for 12 months from the date of receipt of the product under proper storage and handling conditions. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Reference Data | |
| RefSeq | NP_003281 |
| Locus ID | 7171 |
| UniProt ID | P67936, V9HW56 |
| Cytogenetics | 19p13.12-p13.11 |
| Refseq Size | 2645 |
| Refseq ORF | 744 |
| Synonyms | HEL-S-108 |
| Summary | This gene encodes a member of the tropomyosin family of actin-binding proteins involved in the contractile system of striated and smooth muscles and the cytoskeleton of non-muscle cells. Tropomyosins are dimers of coiled-coil proteins that polymerize end-to-end along the major groove in most actin filaments. They provide stability to the filaments and regulate access of other actin-binding proteins. In muscle cells, they regulate muscle contraction by controlling the binding of myosin heads to the actin filament. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2009] |
| Protein Pathways | Cardiac muscle contraction, Dilated cardiomyopathy, Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) |
Documents
| FAQs |
| SDS |
Resources
Recombinant Protein Resources |
Other Versions
| SKU | Description | Size | Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| LC418787 | TPM4 HEK293T cell transient overexpression lysate (as WB positive control) |
USD 134.00 |
|
| LC428735 | TPM4 HEK293T cell transient overexpression lysate (as WB positive control) |
USD 134.00 |
|
| LY418787 | Transient overexpression lysate of tropomyosin 4 (TPM4), transcript variant 2 |
USD 436.00 |
|
| LY428735 | Transient overexpression lysate of tropomyosin 4 (TPM4), transcript variant 1 |
USD 436.00 |
|
| PH301133 | TPM4 MS Standard C13 and N15-labeled recombinant protein (NP_003281) |
USD 3,255.00 |
|
| PH327534 | TPM4 MS Standard C13 and N15-labeled recombinant protein (NP_001138632) |
USD 3,255.00 |
|
| TP327534 | Purified recombinant protein of Homo sapiens tropomyosin 4 (TPM4), transcript variant 1, 20 µg |
USD 867.00 |
{0} Product Review(s)
Be the first one to submit a review






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China