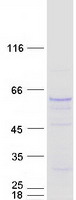
SMOX (NM_175840) Human Mass Spec Standard
CAT#: PH300156
SMOX MS Standard C13 and N15-labeled recombinant protein (NP_787034)
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Tag | C-Myc/DDK |
| Species | Human |
| Expression Host | HEK293 |
| Expression cDNA Clone or AA Sequence | RC200156 |
| Predicted MW | 56.1 kDa |
| Protein Sequence |
>RC200156 protein sequence
Red=Cloning site Green=Tags(s) MQSCESSGDSADDPLSRGLRRRGQPRVVVIGAGLAGLAAAKALLEQGFTDVTVLEASSHIGGRVQSVKLG HATFELGATWIHGSHGNPIYHLAEANGLLEETTDGERSVGRISLYSKNGVACYLTNHGRRIPKDVVEEFS DLYNEVYNLTQEFFRHDKPVNAESQNSVGVFTREEVRNRIRNDPDDPEATKRLKLAMIQQYLKVESCESS SHSMDEVSLSAFGEWTEIPGAHHIIPSGFMRVVELLAEGIPAHVIQLGKPVRCIHWDQASARPRGPEIEP RGVLKRQYTSFFRPGLPTEKVAAIHRLGIGTTDKIFLEFEEPFWGPECNSLQFVWEDEAESHTLTYPPEL WYRKICGFDVLYPPERYGHVLSGWICGEEALVMEKCDDEAVAEICTEMLRQFTGNPNIPKPRRILRSAWG SNPYFRGSYSYTQVGSSGADVEKLAKPLPYTESSKTAPMQVLFSGEATHRKYYSTTHGALLSGQREAARL IEMYRDLFQQGT TRTRPLEQKLISEEDLAANDILDYKDDDDKV |
| Purity | > 80% as determined by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie blue staining |
| Concentration | >0.05 µg/µL as determined by microplate BCA method |
| Labeling Method | Labeled with [U- 13C6, 15N4]-L-Arginine and [U- 13C6, 15N2]-L-Lysine |
| Buffer | 25 mM Tris-HCl, 100 mM glycine, pH 7.3 |
| Storage | Store at -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Stability | Stable for 3 months from receipt of products under proper storage and handling conditions. |
| Reference Data | |
| RefSeq | NP_787034 |
| RefSeq Size | 2090 |
| RefSeq ORF | 1506 |
| Synonyms | C20orf16; PAO; PAO-1; PAO1; PAOH; PAOH1; SMO |
| Locus ID | 54498 |
| UniProt ID | Q9NWM0 |
| Cytogenetics | 20p13 |
| Summary | Polyamines are ubiquitous polycationic alkylamines which include spermine, spermidine, putrescine, and agmatine. These molecules participate in a broad range of cellular functions which include cell cycle modulation, scavenging reactive oxygen species, and the control of gene expression. These molecules also play important roles in neurotransmission through their regulation of cell-surface receptor activity, involvement in intracellular signalling pathways, and their putative roles as neurotransmitters. This gene encodes an FAD-containing enzyme that catalyzes the oxidation of spermine to spermadine and secondarily produces hydrogen peroxide. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoenzymes have been identified for this gene, some of which have failed to demonstrate significant oxidase activity on natural polyamine substrates. The characterized isoenzymes have distinctive biochemical characteristics and substrate specificities, suggesting the existence of additional levels of complexity in polyamine catabolism. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2012] |
| Protein Families | Druggable Genome |
Documents
| FAQs |
| SDS |
Resources
Recombinant Protein Resources |
Other Versions
| SKU | Description | Size | Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| LC406223 | SMOX HEK293T cell transient overexpression lysate (as WB positive control) |
USD 206.00 |
|
| LC406224 | SMOX HEK293T cell transient overexpression lysate (as WB positive control) |
USD 134.00 |
|
| LC406226 | SMOX HEK293T cell transient overexpression lysate (as WB positive control) |
USD 206.00 |
|
| LY406223 | Transient overexpression lysate of spermine oxidase (SMOX), transcript variant 1 |
USD 665.00 |
|
| LY406224 | Transient overexpression lysate of spermine oxidase (SMOX), transcript variant 2 |
USD 436.00 |
|
| LY406226 | Transient overexpression lysate of spermine oxidase (SMOX), transcript variant 4 |
USD 665.00 |
|
| TP300156 | Recombinant protein of human spermine oxidase (SMOX), transcript variant 2, 20 µg |
USD 867.00 |
{0} Product Review(s)
Be the first one to submit a review






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China