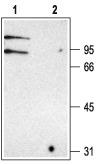
Clcnkb Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
Frequently bought together (1)
Other products for "Clcnkb"
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Applications | WB |
| Recommended Dilution | WB: 1:200-1:2000; IHC: 1:100-1:3000 |
| Reactivities | Rat |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Immunogen | Peptide (C)KKAISTLTNPPAPK, corresponding to amino acid residues 674-687 of rat longer form CLC-K2L. Intracellular, C-terminus. |
| Formulation | Lyophilized. Concentration before lyophilization ~0.8mg/ml (lot dependent, please refer to CoA along with shipment for actual concentration). Buffer before lyophilization: Phosphate buffered saline (PBS), pH 7.4, 1% BSA, 5% sucrose, 0.025% NaN3. |
| Reconstitution Method | Add 50 ul double distilled water (DDW) to the lyophilized powder. |
| Purification | Affinity purified on immobilized antigen. |
| Conjugation | Unconjugated |
| Storage | Store at -20°C as received. |
| Stability | Stable for 12 months from date of receipt. |
| Gene Name | chloride voltage-gated channel Kb |
| Database Link | |
| Background | CLC-Ka and CLC-Kb are members of the voltage-dependent Cl channel (CLC) family that includes nine known members in mammals. The human CLC-Ka and CLC-Kb (known as CLC-K1 and CLC-K2 in the rat) channels are closely related genes that share 94% sequence homology and identical genomic organization. CLC channels can be classified as plasma membrane channels and intracellular organelle channels. The first group includes the CLC-1, CLC-2 CLC-Ka and CLC-Kb channels. The second group comprises the CLC-3, CLC-4, CLC-5, CLC-6 and CLC-7. CLC channels that function in the plasma membrane are involved in the stabilization of membrane potential and in transepithelial transport. The presumed function of the intracellular CLC channels is support of the acidification of the intraorganellar compartment. In this regard, recent reports indicate that ClC-4 and ClC-5 (and by inference ClC-3) can function as Cl/H+ antiporters. The functional unit of the CLC channels is a dimer with each subunit forming a proper pore. Although the crystal structure of bacterial CLC channels was resolved,the topology of the CLC channels is complex and has not been fully elucidated. It is generally accepted that both the N- and C- terminus domains are intracellular while the number and configuration of the transmembrane domains vary greatly between different models. CLC-K channels require the presence of the auxiliary b subunit barttin, a 34 kD transmembrane protein, for transport to the plama membrane and regulation of channel permeation and gating. CLC-K channels are expressed primarily in the kidney from the thin ascending limb to the collecting duct of the nephron, and in the stria vascularis and dark cells of the vestibular organ of the inner ear. The channels are important for renal salt reabsorption and water balance by enabling chloride exit across the basolateral membranes. The importance of the CLC-K channel in renal function is demonstrated by the fact that loss-of-function mutations in CLC-Kb lead to Bartter syndrome type III, an autosomal recessive disorder characterized by severe salt wasting, low blood pressure, hypokalemia and hypercalciuria. |
| Synonyms | ClC-K2; ClC-Kb; CLCKB; hClC-Kb; MGC24087 |
| Reference Data | |
Documents
| Product Manuals |
| FAQs |
| SDS |
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China