GLDC Human Gene Knockout Kit (CRISPR)
CAT#: KN211292BN
GLDC - human gene knockout kit via CRISPR, HDR mediated
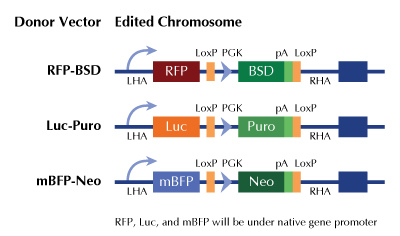
Functional Cassette: GFP-puro Luciferase-Puro RFP-BSD
HDR-mediated knockout kit validation
USD 1,657.00
4 Weeks*
USD 450.00
USD 625.00
USD 1,332.00
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Format | 2 gRNA vectors, 1 mBFP-Neo donor, 1 scramble control |
| Donor DNA | mBFP-Neo |
| Symbol | GLDC |
| Locus ID | 2731 |
| Components |
KN211292G1, GLDC gRNA vector 1 in pCas-Guide CRISPR vector KN211292G2, GLDC gRNA vector 2 in pCas-Guide CRISPR vector KN211292BND, donor DNA containing left and right homologous arms and mBFP-Neo functional cassette. GE100003, scramble sequence in pCas-Guide vector |
| Disclaimer | These products are manufactured and supplied by OriGene under license from ERS. The kit is designed based on the best knowledge of CRISPR technology. The system has been functionally validated for knocking-in the cassette downstream the native promoter. The efficiency of the knock-out varies due to the nature of the biology and the complexity of the experimental process. |
| Reference Data | |
| RefSeq | NM_000170 |
| UniProt ID | P23378 |
| Synonyms | GCE; GCSP; HYGN1 |
| Summary | Degradation of glycine is brought about by the glycine cleavage system, which is composed of four mitochondrial protein components: P protein (a pyridoxal phosphate-dependent glycine decarboxylase), H protein (a lipoic acid-containing protein), T protein (a tetrahydrofolate-requiring enzyme), and L protein (a lipoamide dehydrogenase). The protein encoded by this gene is the P protein, which binds to glycine and enables the methylamine group from glycine to be transferred to the T protein. Defects in this gene are a cause of nonketotic hyperglycinemia (NKH).[provided by RefSeq, Jan 2010] |
Documents
| Product Manuals |
| FAQs |
| SDS |
Resources
Other Versions
| SKU | Description | Size | Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| KN211292 | GLDC - human gene knockout kit via CRISPR, HDR mediated |
USD 1,657.00 |
|
| KN211292LP | GLDC - human gene knockout kit via CRISPR, HDR mediated |
USD 1,657.00 |
|
| KN211292RB | GLDC - human gene knockout kit via CRISPR, HDR mediated |
USD 1,657.00 |
|
| KN411292 | GLDC - KN2.0, Human gene knockout kit via CRISPR, non-homology mediated. |
USD 1,657.00 |
|
| GA101819 | GLDC CRISPRa kit - CRISPR gene activation of human glycine decarboxylase |
USD 1,657.00 |
{0} Product Review(s)
Be the first one to submit a review






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China