Beta crystallin S (CRYGS) (C-term) Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
CAT#: AP51093PU-N
Beta crystallin S (CRYGS) (C-term) rabbit polyclonal antibody, Aff - Purified
Other products for "Beta crystallin S"
Specifications
| Product Data | |
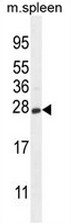
| Applications | WB |
| Recommended Dilution | ELISA: 1/1000. Western blot: 1/100 - 1/500. |
| Reactivities | Human, Mouse |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Isotype | Ig |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Immunogen | KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 136-166 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human CRYGS |
| Specificity | This antibody reacts to human and mouse CRYGS. |
| Formulation | PBS State: Aff - Purified State: Liquid purified Ig fraction Preservative: 0.09% (W/V) sodium azide |
| Concentration | lot specific |
| Purification | Affinity chromatography on Protein A |
| Conjugation | Unconjugated |
| Storage | Store undiluted at 2-8°C for one month or (in aliquots) at -20°C for longer. |
| Stability | Shelf life: one year from despatch. |
| Predicted Protein Size | 21007 Da |
| Gene Name | crystallin gamma S |
| Database Link | |
| Background | Crystallins are separated into two classes: taxon-specific, or enzyme, and ubiquitous. The latter class constitutes the major proteins of vertebrate eye lens and maintains the transparency and refractive index of the lens. Since lens central fiber cells lose their nuclei during development, these crystallins are made and then retained throughout life, making them extremely stable proteins. Mammalian lens crystallins are divided into alpha, beta, and gamma families; beta and gamma crystallins are also considered as a superfamily. Alpha and beta families are further divided into acidic and basic groups. Seven protein regions exist in crystallins: four homologous motifs, a connecting peptide, and N- and C-terminal extensions. Gamma-crystallins are a homogeneous group of highly symmetrical, monomeric proteins typically lacking connecting peptides and terminal extensions. They are differentially regulated after early development. This gene encodes a protein initially considered to be a beta-crystallin but the encoded protein is monomeric and has greater sequence similarity to other gamma-crystallins. This gene encodes the most significant gamma-crystallin in adult eye lens tissue. Whether due to aging or mutations in specific genes, gamma-crystallins have been involved in cataract formation. |
| Synonyms | Gamma-crystallin S, Gamma-S-crystallin, CRYGS, GRYG8 |
| Reference Data | |
Documents
| Product Manuals |
| FAQs |
| SDS |
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China