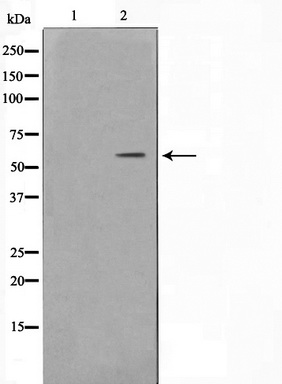
c-Myc (MYC) Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
USD 436.00
USD 200.00
USD 867.00
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Applications | IHC, WB |
| Recommended Dilution | WB: 1:500-1:2000; IHC: 1:50-1:200 |
| Reactivities | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human C-myc |
| Formulation | Rabbit IgG in phosphate buffered saline , pH 7.4, 150mM NaCl, 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
| Concentration | lot specific |
| Purification | The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific peptide. |
| Conjugation | Unconjugated |
| Storage | Store at -20°C as received. |
| Stability | Stable for 12 months from date of receipt. |
| Gene Name | v-myc avian myelocytomatosis viral oncogene homolog |
| Database Link | |
| Background | Members of the Myc/Max/Mad network function as transcriptional regulators with roles in various aspects of cell behavior including proliferation, differentiation and apoptosis . These proteins share a common basic-helix-loop-helix leucine zipper (bHLH-ZIP) motif required for dimerization and DNA-binding. Max was originally discovered based on its ability to associate with c-Myc and found to be required for the ability of Myc to bind DNA and activate transcription. Subsequently, Max has been viewed as a central component of the transcriptional network, forming homodimers as well as heterodimers with other members of the Myc and Mad families. The association between Max and either Myc or Mad can have opposing effects on transcriptional regulation and cell behavior. The Mad family consists of four related proteins; Mad1, Mad2 (Mxi1), Mad3 and Mad4, and the more distantly related members of the bHLH-ZIP family, Mnt and Mga. Like Myc, the Mad proteins are tightly regulated with short half-lives. In general, Mad family members interfere with Myc-mediated processes such as proliferation, transformation and prevention of apoptosis by inhibiting transcription. |
| Synonyms | bHLHe39; c-Myc; MRTL; MYCC |
| Reference Data | |
| Protein Families | Druggable Genome, Embryonic stem cells, Induced pluripotent stem cells, Stem cell - Pluripotency, Stem cell relevant signaling - JAK/STAT signaling pathway, Stem cell relevant signaling - TGFb/BMP signaling pathway, Stem cell relevant signaling - Wnt Signaling pathway, Transcription Factors |
| Protein Pathways | Acute myeloid leukemia, Bladder cancer, Cell cycle, Chronic myeloid leukemia, Colorectal cancer, Endometrial cancer, ErbB signaling pathway, Jak-STAT signaling pathway, MAPK signaling pathway, Pathways in cancer, Small cell lung cancer, TGF-beta signaling pathway, Thyroid cancer, Wnt signaling pathway |
Documents
| Product Manuals |
| FAQs |
| SDS |
{0} Product Review(s)
Be the first one to submit a review






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China