HSD17B1 (NM_000413) Human Recombinant Protein
CAT#: TP762706
Purified recombinant protein of Human hydroxysteroid (17-beta) dehydrogenase 1 (HSD17B1), 2Ala-End, with N-terminal His tag, expressed in E.coli, 50ug
Frequently bought together (1)
Other products for "HSD17B1"
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Species | Human |
| Expression Host | E. coli |
| Expression cDNA Clone or AA Sequence |
A DNA sequence encoding the region (2Ala-End) of HSD17B1
|
| Tag | N-His |
| Predicted MW | 37.1 kDa |
| Concentration | >0.05 ug/ul as determined by microplate BCA method |
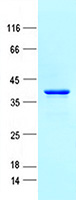
| Purity | > 80% as determined by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie blue staining |
| Buffer | 25mM Tris, 150mM NaCl, 10% glycerol, pH8.0, 1% SKL |
| Storage | Store at -80°C after receiving vials. |
| Stability | Stable for at least 1 year from receipt of products under proper storage and handling conditions. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Reference Data | |
| RefSeq | NP_000404 |
| Locus ID | 3292 |
| UniProt ID | P14061 |
| Cytogenetics | 17q21.2 |
| Refseq Size | 2248 |
| Refseq ORF | 984 |
| Synonyms | 17-beta-HSD; 20-alpha-HSD; E2DH; EDH17B2; EDHB17; HSD17; SDR28C1 |
| Summary | This gene encodes a member of the 17beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase family of short-chain dehydrogenases/reductases. It has a dual function in estrogen activation and androgen inactivation and plays a major role in establishing the estrogen E2 concentration gradient between serum and peripheral tissues. The encoded protein catalyzes the last step in estrogen activation, using NADPH to convert estrogens E1 and E2 and androgens like 4-androstenedione, to testosterone. It has an N-terminal short-chain dehydrogenase domain with a cofactor binding site, and a narrow, hydrophobic C-terminal domain with a steroid substrate binding site. This gene is expressed primarily in the placenta and ovarian granulosa cells, and to a lesser extent, in the endometrium, adipose tissue, and prostate. Polymorphisms in this gene have been linked to breast and prostate cancer. A pseudogene of this gene has been identified. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2016] |
| Protein Families | Druggable Genome |
| Protein Pathways | Androgen and estrogen metabolism, Metabolic pathways |
Documents
| FAQs |
| SDS |
Resources
Recombinant Protein Resources |
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China