GLIS2 (NM_032575) Human Recombinant Protein
CAT#: TP761497
Purified recombinant protein of Human GLIS family zinc finger 2 (GLIS2), full length, with N-terminal HIS tag, expressed in E. coli, 50ug
Frequently bought together (1)
Other products for "GLIS2"
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Species | Human |
| Expression Host | E. coli |
| Expression cDNA Clone or AA Sequence |
A DNA sequence encoding human full-length GLIS2
|
| Tag | N-His |
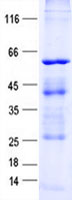
| Predicted MW | 55.5 kDa |
| Concentration | >0.05 µg/µL as determined by microplate BCA method |
| Purity | > 80% as determined by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie blue staining |
| Buffer | 25 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.0, 150 mM NaCl, 1% sarkosyl, 10% glycerol |
| Note | For testing in cell culture applications, please filter before use. Note that you may experience some loss of protein during the filtration process. |
| Storage | Store at -80°C. |
| Stability | Stable for 12 months from the date of receipt of the product under proper storage and handling conditions. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Reference Data | |
| RefSeq | NP_115964 |
| Locus ID | 84662 |
| UniProt ID | Q9BZE0 |
| Cytogenetics | 16p13.3 |
| Refseq Size | 3705 |
| Refseq ORF | 1572 |
| Synonyms | NKL; NPHP7 |
| Summary | This gene is a member of the GLI-similar zinc finger protein family and encodes a nuclear transcription factor with five C2H2-type zinc finger domains. The protein encoded by this gene is widely expressed at low levels in the neural tube and peripheral nervous system and likely promotes neuronal differentiation. It is abundantly expressed in the kidney and may have a role in the regulation of kidney morphogenesis. p120 regulates the expression level of this protein and induces the cleavage of this protein's C-terminal zinc finger domain. This protein also promotes the nuclear translocation of p120. Mutations in this gene cause nephronophthisis (NPHP), an autosomal recessive kidney disease characterized by tubular basement membrane disruption, interstitial lymphohistiocytic cell infiltration, and development of cysts at the corticomedullary border of the kidneys.[provided by RefSeq, Jan 2010] |
| Protein Families | ES Cell Differentiation/IPS |
Documents
| FAQs |
| SDS |
Resources
Recombinant Protein Resources |
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China