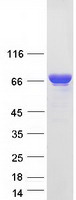
FUBP1 (NM_003902) Human Mass Spec Standard
CAT#: PH315674
FUBP1 MS Standard C13 and N15-labeled recombinant protein (NP_003893)
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Tag | C-Myc/DDK |
| Species | Human |
| Expression Host | HEK293 |
| Expression cDNA Clone or AA Sequence | RC215674 |
| Predicted MW | 67.4 kDa |
| Protein Sequence |
>RC215674 representing NM_003902
Red=Cloning site Green=Tags(s) MADYSTVPPPSSGSAGGGGGGGGGGGVNDAFKDALQRARQIAAKIGGDAGTSLNSNDYGYGGQKRPLEDG DQPDAKKVAPQNDSFGTQLPPMHQQQSRSVMTEEYKVPDGMVGFIIGRGGEQISRIQQESGCKIQIAPDS GGLPERSCMLTGTPESVQSAKRLLDQIVEKGRPAPGFHHGDGPGNAVQEIMIPASKAGLVIGKGGETIKQ LQERAGVKMVMIQDGPQNTGADKPLRITGDPYKVQQAKEMVLELIRDQGGFREVRNEYGSRIGGNEGIDV PIPRFAVGIVIGRNGEMIKKIQNDAGVRIQFKPDDGTTPERIAQITGPPDRCQHAAEIITDLLRSVQAGN PGGPGPGGRGRGRGQGNWNMGPPGGLQEFNFIVPTGKTGLIIGKGGETIKSISQQSGARIELQRNPPPNA DPNMKLFTIRGTPQQIDYARQLIEEKIGGPVNPLGPPVPHGPHGVPGPHGPPGPPGPGTPMGPYNPAPYN PGPPGPAPHGPPAPYAPQGWGNAYPHWQQQAPPDPAKAGTDPNSAAWAAYYAHYYQQQAQPPPAAPAGAP TTTQTNGQGDQQNPAPAGQVDYTKAWEEYYKKMGQAVPAPTGAPPGGQPDYSAAWAEYYRQQAAYYAQTS PQGMPQHPPAPQGQ TRTRPLEQKLISEEDLAANDILDYKDDDDKV |
| Purity | > 80% as determined by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie blue staining |
| Concentration | >0.05 µg/µL as determined by microplate BCA method |
| Labeling Method | Labeled with [U- 13C6, 15N4]-L-Arginine and [U- 13C6, 15N2]-L-Lysine |
| Buffer | 25 mM Tris-HCl, 100 mM glycine, pH 7.3 |
| Storage | Store at -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Stability | Stable for 3 months from receipt of products under proper storage and handling conditions. |
| Reference Data | |
| RefSeq | NP_003893 |
| RefSeq Size | 2884 |
| RefSeq ORF | 1932 |
| Synonyms | FBP; FUBP; hDH V |
| Locus ID | 8880 |
| UniProt ID | Q96AE4 |
| Cytogenetics | 1p31.1 |
| Summary | The protein encoded by this gene is a single stranded DNA-binding protein that binds to multiple DNA elements, including the far upstream element (FUSE) located upstream of c-myc. Binding to FUSE occurs on the non-coding strand, and is important to the regulation of c-myc in undifferentiated cells. This protein contains three domains, an amphipathic helix N-terminal domain, a DNA-binding central domain, and a C-terminal transactivation domain that contains three tyrosine-rich motifs. The N-terminal domain is thought to repress the activity of the C-terminal domain. This protein is also thought to bind RNA, and contains 3'-5' helicase activity with in vitro activity on both DNA-DNA and RNA-RNA duplexes. Aberrant expression of this gene has been found in malignant tissues, and this gene is important to neural system and lung development. Binding of this protein to viral RNA is thought to play a role in several viral diseases, including hepatitis C and hand, foot and mouth disease. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2014] |
| Protein Families | Stem cell - Pluripotency, Transcription Factors |
Documents
| FAQs |
| SDS |
Resources
Recombinant Protein Resources |
Other Versions
| SKU | Description | Size | Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| LC418358 | FUBP1 HEK293T cell transient overexpression lysate (as WB positive control) |
USD 134.00 |
|
| LY418358 | Transient overexpression lysate of far upstream element (FUSE) binding protein 1 (FUBP1) |
USD 436.00 |
|
| TP315674 | Recombinant protein of human far upstream element (FUSE) binding protein 1 (FUBP1), 20 µg |
USD 867.00 |
{0} Product Review(s)
Be the first one to submit a review






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China