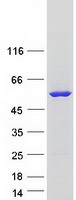
FMO3 (NM_001002294) Human Mass Spec Standard
CAT#: PH312376
FMO3 MS Standard C13 and N15-labeled recombinant protein (NP_001002294)
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Tag | C-Myc/DDK |
| Species | Human |
| Expression Host | HEK293 |
| Expression cDNA Clone or AA Sequence | RC212376 |
| Predicted MW | 59.9 kDa |
| Protein Sequence |
>RC212376 representing NM_001002294
Red=Cloning site Green=Tags(s) MGKKVAIIGAGVSGLASIRSCLEEGLEPTCFEKSNDIGGLWKFSDHAEEGRASIYKSVFSNSSKEMMCFP DFPFPDDFPNFMHNSKIQEYIIAFAKEKNLLKYIQFKTFVSSVNKHPDFATTGQWDVTTERDGKKESAVF DAVMVCSGHHVYPNLPKESFPGLNHFKGKCFHSRDYKEPGVFNGKRVLVVGLGNSGCDIATELSRTAEQV MISSRSGSWVMSRVWDNGYPWDMLLVTRFGTFLKNNLPTAISDWLYVKQMNARFKHENYGLMPLNGVLRK EPVFNDELPASILCGIVSVKPNVKEFTETSAIFEDGTIFEGIDCVIFATGYSFAYPFLDESIIKSRNNEI ILFKGVFPPLLEKSTIAVIGFVQSLGAAIPTVDLQSRWAAQVIKGTCTLPSMEDMMNDINEKMEKKRKWF GKSETIQTDYIVYMDELSSFIGAKPNIPWLFLTDPKLAMEVYFGPCSPYQFRLVGPGQWPGARNAILTQW DRSLKPMQTRVVGRLQKPCFFFHWLKLFAIPILLIAVFLVLT TRTRPLEQKLISEEDLAANDILDYKDDDDKV |
| Purity | > 80% as determined by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie blue staining |
| Concentration | >0.05 µg/µL as determined by microplate BCA method |
| Labeling Method | Labeled with [U- 13C6, 15N4]-L-Arginine and [U- 13C6, 15N2]-L-Lysine |
| Buffer | 25 mM Tris-HCl, 100 mM glycine, pH 7.3 |
| Storage | Store at -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Stability | Stable for 3 months from receipt of products under proper storage and handling conditions. |
| Reference Data | |
| RefSeq | NP_001002294 |
| RefSeq Size | 2070 |
| RefSeq ORF | 1596 |
| Synonyms | dJ127D3.1; FMOII; TMAU |
| Locus ID | 2328 |
| UniProt ID | P31513, A0A024R8Z4, Q53FW5 |
| Cytogenetics | 1q24.3 |
| Summary | Flavin-containing monooxygenases (FMO) are an important class of drug-metabolizing enzymes that catalyze the NADPH-dependent oxygenation of various nitrogen-,sulfur-, and phosphorous-containing xenobiotics such as therapeutic drugs, dietary compounds, pesticides, and other foreign compounds. The human FMO gene family is composed of 5 genes and multiple pseudogenes. FMO members have distinct developmental- and tissue-specific expression patterns. The expression of this FMO3 gene, the major FMO expressed in adult liver, can vary up to 20-fold between individuals. This inter-individual variation in FMO3 expression levels is likely to have significant effects on the rate at which xenobiotics are metabolised and, therefore, is of considerable interest to the pharmaceutical industry. This transmembrane protein localizes to the endoplasmic reticulum of many tissues. Alternative splicing of this gene results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. Mutations in this gene cause the disorder trimethylaminuria (TMAu) which is characterized by the accumulation and excretion of unmetabolized trimethylamine and a distinctive body odor. In healthy individuals, trimethylamine is primarily converted to the non odorous trimethylamine N-oxide.[provided by RefSeq, Jan 2016] |
| Protein Families | Druggable Genome, Transmembrane |
| Protein Pathways | Drug metabolism - cytochrome P450 |
Documents
| FAQs |
| SDS |
Resources
Recombinant Protein Resources |
Other Versions
| SKU | Description | Size | Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| LC416335 | FMO3 HEK293T cell transient overexpression lysate (as WB positive control) |
USD 134.00 |
|
| LC424145 | FMO3 HEK293T cell transient overexpression lysate (as WB positive control) |
USD 206.00 |
|
| LY416335 | Transient overexpression lysate of flavin containing monooxygenase 3 (FMO3), transcript variant 1 |
USD 436.00 |
|
| LY424145 | Transient overexpression lysate of flavin containing monooxygenase 3 (FMO3), transcript variant 2 |
USD 665.00 |
|
| PH306506 | FMO3 MS Standard C13 and N15-labeled recombinant protein (NP_008825) |
USD 3,255.00 |
|
| TP306506 | Recombinant protein of human flavin containing monooxygenase 3 (FMO3), transcript variant 1, 20 µg |
USD 867.00 |
|
| TP312376 | Recombinant protein of human flavin containing monooxygenase 3 (FMO3), transcript variant 2, 20 µg |
USD 867.00 |
{0} Product Review(s)
Be the first one to submit a review






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China