AIF (AIFM1) Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
USD 436.00
USD 200.00
USD 867.00
Specifications
| Product Data | |
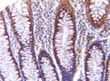
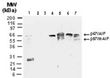
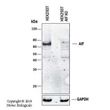
| Applications | IHC, IP, Simple Western, WB |
| Recommended Dilution | Immunohistochemistry, Immunoprecipitation: 1:50-1:200, Western Blot: 1:1000-1:2000~, Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: 1:1000-1:5000~, Immunohistochemistry-Frozen: 1:1000-1:5000, Simple Western: 1:500, Knockout Validated |
| Reactivities | Human, Mouse, Rat, Bovine, Canine |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Immunogen | (aa 151-170); human |
| Formulation | Store at 4C short term. Aliquot and store at -20C long term. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Concentration | lot specific |
| Purification | Whole antisera |
| Conjugation | Unconjugated |
| Storage | Store at -20°C as received. |
| Stability | Stable for 12 months from date of receipt. |
| Gene Name | apoptosis inducing factor, mitochondria associated 1 |
| Database Link | |
| Background | AIF (apoptosis-inducing factor) was initially discovered as a protein involved in caspase-independent cell death. It is now known that AIF has both vital and lethal functions (reviewed in Modjtahedi et al, 2006). In healthy cells, AIF is a flavoprotein present in the mitochondria where it has vital roles in cellular redox metabolism and mitochondrial bioenergetics. In many models of apoptosis, AIF is released from the mitochondria during mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization along with other mitochondrial proteins. Upon release, AIF translocates first to the cytosol and then to the nucleus where it induces chromatin condensation and DNA degradation. Although several lines of evidence suggest that AIF is a main mediator of capsase-independent cell death, the mechanisms regulating AIF pro-apoptotic function remain to be fully elucidatied and may depend on the cell type and type of apoptotic stimuli. Human AIF is transcribed from a nuclear gene located on the X chromosome and translated in the cytoplasm to a precursor protein of 613 amino acids (aa) which corresponds to ~67 kDa. The precursor protein is imported into the mitochonria by mitochondrial localization sequences located within the N-terminal prodomain of AIF. Once inside the mitochondria, the prodomain is cleaved giving rise to a mature AIF form of ~57 kDa. AIF isoforms generated from a single AIF gene have been identified, including AIF short isoform 2 (324 aa protein; GenBank no. AAY84739.1) and AIF short isoform 3 (237 aa protein; GenBank noAAY84741.1 (reviewed in Delttre et al, 2006). The generation of multiple isoforms from a common gene is an evolutionary mechanism that increases protein diversiity in eukaryotes. Regulating gene expression through the production of multiple isoforms from a single gene is thought to play a major role in the control of apoptosis and other forms of programmed cell death. It recognizes AIF and AIF isoforms containing the peptide immunogen sequence, RARDPGARVLIVSEDPELP. |
| Synonyms | AIF; CMT2D; CMTX4; COWCK; COXPD6; NADMR; NAMSD; PDCD8 |
| Reference Data | |
| Protein Families | Druggable Genome, Transmembrane |
| Protein Pathways | Apoptosis |
Documents
| Product Manuals |
| FAQs |
| SDS |
{0} Product Review(s)
Be the first one to submit a review






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China