Slc6a9 Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
Frequently bought together (1)
beta Actin Mouse Monoclonal Antibody, Clone OTI1, Loading Control
USD 200.00
Other products for "Slc6a9"
Specifications
| Product Data | |
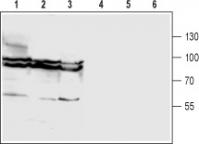
| Applications | WB |
| Recommended Dilution | WB: 1:200-1:2000 |
| Reactivities | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Immunogen | Peptide (C)RLYVLKLSDDIGD, corresponding to amino acid residues 202-214 of rat Glycine Transporter 1. 2nd extracellular loop. |
| Formulation | Lyophilized. Concentration before lyophilization ~0.8mg/ml (lot dependent, please refer to CoA along with shipment for actual concentration). Buffer before lyophilization: Phosphate buffered saline (PBS), pH 7.4, 1% BSA, 0.05% NaN3. |
| Reconstitution Method | Add 50 ul double distilled water (DDW) to the lyophilized powder. |
| Purification | Affinity purified on immobilized antigen. |
| Conjugation | Unconjugated |
| Storage | Store at -20°C as received. |
| Stability | Stable for 12 months from date of receipt. |
| Gene Name | solute carrier family 6 member 9 |
| Database Link | |
| Background | Apart from its obvious biochemical functions, glycine is also an important inhibitory neurotransmitter. Following depolarization, glycine is released from synaptic vesicles, binds to glycine receptors (GlyRs) on postsynaptic membranes thereby causing hyperpolarization of postsynaptic neurons due to the massive influx of Cl ions. Glycine is then taken up from the synaptic cleft via the glycine transporters GlyT1 and GlyT2 . GlyT1 and GlyT2 belong to the SLC6, Na+/Cl dependent transporter family, of which members include transporters for GABA, serotonin, dopamine and norepinephrine. Like all SLC6 members, GlyT1 and GlyT2 have 12 transmembrane domains and intracellular N- and C-terminals. Both can be found in different splice variants. SLC6 transporters undergo post-translational modifications. For instance, GlyT1 and GlyT2 are glycosylated, which is important for their membrane trafficking. Phosphorylation of these two transporters also takes place in a PKC-dependent manner, which may lead to down regulation of both transporters. Pharmacologically, GlyT1 and GlyT2 can be differentiated by applying sarcosine which inhibits GlyT1 but not GlyT2 . GlyT1 and GlyT2 are broadly expressed in the nervous system; GlyT1 is concentrated in glial cells, while GlyT2 is present in glycenergic neurons in the spinal cord, brainstem and cerebellum. GlyT1 can also be detected in the pancreas, uterus, stomach, spleen, liver and retina. GlyT1 has become a target for the treatment of schizophrenia, although a defect of the protein is not directly associated with the disorder. Inhibiting GlyT1 should lead to the increase in glutamatergic pathways, thereby decreasing psychotic effects in schizophrenic individuals. GlyT2 has been associated with hyperekplexia, a motor disorder characterized by neonatal hypertonia and startle reflex. |
| Synonyms | DKFZp547A1118; GlyT-1; GLYT1 |
| Reference Data | |
Documents
| Product Manuals |
| FAQs |
| SDS |
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China