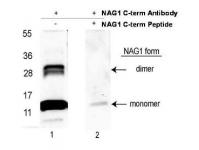
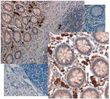
GDF15 Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
Frequently bought together (2)
beta Actin Mouse Monoclonal Antibody, Clone OTI1, Loading Control
USD 200.00
Other products for "GDF15"
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Applications | IHC, WB |
| Recommended Dilution | ELISA: 1:10,000-1:50,000, WB: 1:1,000-1:5,000, IHC: 1:500-1:2,500 |
| Reactivities | Human, Mouse |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Immunogen | Anti-NAG-1 (C-terminal specific) antibody was prepared by repeated immunizations with a synthetic peptide corresponding to a region near the carboxy terminal end of human NAG-1 protein. A residue of cysteine was added to facilitate coupling to KLH. |
| Formulation | 0.02 M Potassium Phosphate, 0.15 M Sodium Chloride, pH 7.2 |
| Concentration | lot specific |
| Conjugation | Peroxidase |
| Storage | Store at -20°C as received. |
| Stability | Stable for 12 months from date of receipt. |
| Gene Name | growth differentiation factor 15 |
| Database Link | |
| Synonyms | GDF-15; MIC-1; MIC1; NAG-1; PDF; PLAB; PTGFB |
| Note | Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) activated gene (NAG-1) is a member of the transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) superfamily. NAG-1 is also known as Macrophage Inhibitory Cytokine-1 (MIC-1), Growth Differentiation Factor 15 (GDF15), Placental Bone Morphogenetic Protein (PLAB), or Prostate Derived Factor (PDF). NAG-1 is expressed in human placenta, prostate and colon. It possesses antitumorigenic and proapoptotic activities. NAG-1 expression is dramatically increased in inflammation, injury and malignancy. Increase of NAG-1 expression is a feature of many cancers including breast, colon, pancreas and prostate. In a number of studies, NAG-1 expression was increased by a number of NSAIDs. This increase in expression may correlate with the chemopreventive effect NSAIDs seem to have with certain cancers. NAG-1 expression is also induced by PPAR gamma ligands and by several dietary compounds such as conjugated linoleic acids (CLAs), naturally occurring fatty acids in ruminant food products, indoles, epicatechin gallate, and genistein. Induced expression of NAG-1 results in stimulation of apoptosis and inhibition of cell growth. Inhibition of NAG-1 induced expression by small interference RNA (siRNA) results in repression of induced apoptosis. NAG-1 expression is regulated by a numbers of transcription factors such as ERG-1 and Sp1. EGR-1 may be necessary for NSAID-induced NAG-1 expression. The study of expression of NAG-1 proteins, including variants, is important to define their potential role as serum biomarkers for cancer diagnosis, treatment monitoring, epidemiology study, and nutrition surveys. |
| Reference Data | |
| Protein Families | Druggable Genome, Secreted Protein |
Documents
| Product Manuals |
| FAQs |
| SDS |
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China