FANCA (NM_001018112) Human Recombinant Protein
CAT#: TP761743
Purified recombinant protein of Human Fanconi anemia, complementation group A (FANCA), transcript variant 2, full length, with N-terminal His tag, expressed in E. coli, 50ug
Frequently bought together (1)
Other products for "FANCA"
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Species | Human |
| Expression Host | E. coli |
| Expression cDNA Clone or AA Sequence |
A DNA sequence encoding human full-length FANCA
|
| Tag | N-His |
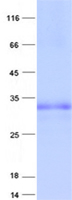
| Predicted MW | 32.8 kDa |
| Concentration | >0.05 µg/µL as determined by microplate BCA method |
| Purity | > 80% as determined by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie blue staining |
| Buffer | 50 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.0, 8 M urea |
| Note | For testing in cell culture applications, please filter before use. Note that you may experience some loss of protein during the filtration process. |
| Storage | Store at -80°C. |
| Stability | Stable for 12 months from the date of receipt of the product under proper storage and handling conditions. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Reference Data | |
| RefSeq | NP_001018122 |
| Locus ID | 2175 |
| UniProt ID | O15360 |
| Cytogenetics | 16q24.3 |
| Refseq Size | 1673 |
| Refseq ORF | 891 |
| Synonyms | FA; FA-H; FA1; FAA; FACA; FAH; FANCH |
| Summary | The Fanconi anemia complementation group (FANC) currently includes FANCA, FANCB, FANCC, FANCD1 (also called BRCA2), FANCD2, FANCE, FANCF, FANCG, FANCI, FANCJ (also called BRIP1), FANCL, FANCM and FANCN (also called PALB2). The previously defined group FANCH is the same as FANCA. Fanconi anemia is a genetically heterogeneous recessive disorder characterized by cytogenetic instability, hypersensitivity to DNA crosslinking agents, increased chromosomal breakage, and defective DNA repair. The members of the Fanconi anemia complementation group do not share sequence similarity; they are related by their assembly into a common nuclear protein complex. This gene encodes the protein for complementation group A. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. Mutations in this gene are the most common cause of Fanconi anemia. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| Protein Families | Druggable Genome |
Documents
| FAQs |
| SDS |
Resources
Recombinant Protein Resources |
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China