Cystatin-C (27-146, His-tag) Human Protein
Other products for "CST3"
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Species | Human |
| Expression Host | E. coli |
| Expression cDNA Clone or AA Sequence |
MGSSHHHHHH SSGLVPRGSH MSSPGKPPRL VGGPMDASVE EEGVRRALDF AVGEYNKASN DMYHSRALQV VRARKQIVAG VNYFLDVELG RTTCTKTQPN LDNCPFHDQP HLKRKAFCSF QIYAVPWQGT MTLSKSTCQD A
|
| Tag | His-tag |
| Predicted MW | 15 kDa |
| Concentration | lot specific |
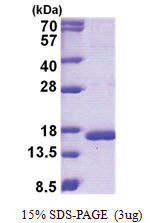
| Purity | >95% by SDS - PAGE |
| Presentation | Purified |
| Buffer | Presentation State: Purified State: Liquid purified protein Buffer System: 20 mM Tris-HCl buffer (pH 8.0) containing 0.1M NaCl, 20% glycerol. |
| Preparation | Liquid purified protein |
| Protein Description | Recombinant human CST3 protein, fused to His-tag at N-terminus, was expressed in E.coli and purified by using conventional chromatography techniques. |
| Storage | Store undiluted at 2-8°C for one week or (in aliquots) at -20°C to -80°C for longer. Avoid repeated freezing and thawing. |
| Stability | Shelf life: one year from despatch. |
| Reference Data | |
| RefSeq | NP_000090 |
| Locus ID | 1471 |
| UniProt ID | P01034, A0A0K0K1J1 |
| Cytogenetics | 20p11.21 |
| Synonyms | ARMD11; HEL-S-2 |
| Summary | The cystatin superfamily encompasses proteins that contain multiple cystatin-like sequences. Some of the members are active cysteine protease inhibitors, while others have lost or perhaps never acquired this inhibitory activity. There are three inhibitory families in the superfamily, including the type 1 cystatins (stefins), type 2 cystatins and the kininogens. The type 2 cystatin proteins are a class of cysteine proteinase inhibitors found in a variety of human fluids and secretions, where they appear to provide protective functions. The cystatin locus on chromosome 20 contains the majority of the type 2 cystatin genes and pseudogenes. This gene is located in the cystatin locus and encodes the most abundant extracellular inhibitor of cysteine proteases, which is found in high concentrations in biological fluids and is expressed in virtually all organs of the body. A mutation in this gene has been associated with amyloid angiopathy. Expression of this protein in vascular wall smooth muscle cells is severely reduced in both atherosclerotic and aneurysmal aortic lesions, establishing its role in vascular disease. In addition, this protein has been shown to have an antimicrobial function, inhibiting the replication of herpes simplex virus. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding a single protein. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2014] |
| Protein Families | Druggable Genome, ES Cell Differentiation/IPS, Transmembrane |
Documents
| FAQs |
| SDS |
Resources
Recombinant Protein Resources |
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China