FUBP1 (279-448, His-tag) Human Protein
Other products for "FUBP1"
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Species | Human |
| Expression Host | E. coli |
| Expression cDNA Clone or AA Sequence |
MGSSHHHHHH SSGLVPRGSH MGSHMDVPIP RFAVGIVIGR NGEMIKKIQN DAGVRIQFKP DDGTTPERIA QITGPPDRCQ HAAEIITDLL RSVQAGNPGG PGPGGRGRGR GQGNWNMGPP GGLQEFNFIV PTGKTGLIIG KGGETIKSIS QQSGARIELQ RNPPPNADPN MKLFTIRGTP QQIDYARQLI EEKIG
|
| Tag | His-tag |
| Predicted MW | 20.8 kDa |
| Concentration | lot specific |
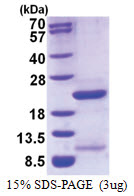
| Purity | >85% by SDS - PAGE |
| Presentation | Purified |
| Buffer | Presentation State: Purified State: Liquid purified protein Buffer System: 20 mM Tris-HCl buffer (pH 8.0) containing 10% glycerol 0.15M NaCl, 1 mM DTT |
| Preparation | Liquid purified protein |
| Protein Description | Recombinant human FUBP1 protein, fused to His-tag at N-terminus, was expressed in E.coli and purified by using conventional chromatography techniques. |
| Storage | Store undiluted at 2-8°C for one week or (in aliquots) at -20°C to -80°C for longer. Avoid repeated freezing and thawing. |
| Stability | Shelf life: one year from despatch. |
| Reference Data | |
| RefSeq | NP_001290362 |
| Locus ID | 8880 |
| UniProt ID | Q96AE4, B4DT31 |
| Cytogenetics | 1p31.1 |
| Synonyms | FBP; FUBP; hDH V |
| Summary | The protein encoded by this gene is a single stranded DNA-binding protein that binds to multiple DNA elements, including the far upstream element (FUSE) located upstream of c-myc. Binding to FUSE occurs on the non-coding strand, and is important to the regulation of c-myc in undifferentiated cells. This protein contains three domains, an amphipathic helix N-terminal domain, a DNA-binding central domain, and a C-terminal transactivation domain that contains three tyrosine-rich motifs. The N-terminal domain is thought to repress the activity of the C-terminal domain. This protein is also thought to bind RNA, and contains 3'-5' helicase activity with in vitro activity on both DNA-DNA and RNA-RNA duplexes. Aberrant expression of this gene has been found in malignant tissues, and this gene is important to neural system and lung development. Binding of this protein to viral RNA is thought to play a role in several viral diseases, including hepatitis C and hand, foot and mouth disease. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2014] |
| Protein Families | Stem cell - Pluripotency, Transcription Factors |
Documents
| FAQs |
| SDS |
Resources
Recombinant Protein Resources |
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China