HSPB1 / HSP27 (1-205, His-tag) Human Protein
Other products for "HSPB1"
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Species | Human |
| Expression Host | E. coli |
| Expression cDNA Clone or AA Sequence |
MGSSHHHHHH SSGLVPRGSH MTERRVPFSL LRGPSWDPFR DWYPHSRLFD QAFGLPRLPE EWSQWLGGSS WPGYVRPLPP AAIESPAVAA PAYSRALSRQ LSSGVSEIRH TADRWRVSLD VNHFAPDELT VKTKDGVVEI TGKHEERQDE HGYISRCFTR KYTLPPGVDP TQVSSSLSPE GTLTVEAPMP KLATQSNEIT IPVTFESRAQ LGGPEAAKSD ETAAK
|
| Tag | His-tag |
| Concentration | lot specific |
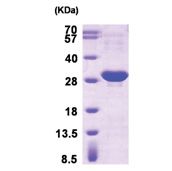
| Purity | >95% by SDS - PAGE |
| Presentation | Purified |
| Buffer | Presentation State: Purified State: Liquid purified protein Buffer System: 20 mM Tris-HCl buffer (pH 8.0) contining 1 mM DTT, 10% glycerol |
| Endotoxin | < 1.0 EU per 1 µg of protein (determined by LAL method ) |
| Preparation | Liquid purified protein |
| Protein Description | Recombinant human HSP27 protein, fused to His-tag at N-terminus, was expressed in E.coli and purified by using conventional chromatography techniques. |
| Storage | Store undiluted at 2-8°C for up to two weeks or (in aliquots) at -20°C or -70°C for longer. Avoid repeated freezing and thawing. |
| Stability | Shelf life: one year from despatch. |
| Reference Data | |
| RefSeq | NP_001531 |
| Locus ID | 3315 |
| UniProt ID | P04792, V9HW43 |
| Cytogenetics | 7q11.23 |
| Synonyms | CMT2F; HEL-S-102; HMN2B; HS.76067; Hsp25; HSP27; HSP28; SRP27 |
| Summary | This gene encodes a member of the small heat shock protein (HSP20) family of proteins. In response to environmental stress, the encoded protein translocates from the cytoplasm to the nucleus and functions as a molecular chaperone that promotes the correct folding of other proteins. This protein plays an important role in the differentiation of a wide variety of cell types. Expression of this gene is correlated with poor clinical outcome in multiple human cancers, and the encoded protein may promote cancer cell proliferation and metastasis, while protecting cancer cells from apoptosis. Mutations in this gene have been identified in human patients with Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease and distal hereditary motor neuropathy. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2017] |
| Protein Pathways | MAPK signaling pathway, VEGF signaling pathway |
Documents
| FAQs |
| SDS |
Resources
Recombinant Protein Resources |
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China