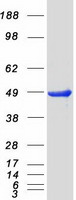
PRKAR2B (NM_002736) Human Mass Spec Standard
CAT#: PH309900
PRKAR2B MS Standard C13 and N15-labeled recombinant protein (NP_002727)
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Tag | C-Myc/DDK |
| Species | Human |
| Expression Host | HEK293 |
| Expression cDNA Clone or AA Sequence | RC209900 |
| Predicted MW | 46.3 kDa |
| Protein Sequence |
>RC209900 protein sequence
Red=Cloning site Green=Tags(s) MSIEIPAGLTELLQGFTVEVLRHQPADLLEFALQHFTRLQQENERKGTARFCHEGRTWGDLGAAAGGGTP SKGVNFAEEPMQSDSEDGEEEEAAPADAGAFNAPVINRFTRRASVCAEAYNPDEEEDDAESRIIHPKTDD QRNRLQEACKDILLFKNLDPEQMSQVLDAMFEKLVKDGEHVIDQGDDGDNFYVIDRGTFDIYVKCDGVGR CVGNYDNRGSFGELALMYNTPRAATITATSPGALWGLDRVTFRRIIVKNNAKKRKMYESFIESLPFLKSL EFSERLKVVDVIGTKVYNDGEQIIAQGDSADSFFIVESGEVKITMKRKGKSEVEENGAVEIARCSRGQYF GELALVTNKPRAASAHAIGTVKCLAMDVQAFERLLGPCMEIMKRNIATYEEQLVALFGTNMDIVEPTA TRTRPLEQKLISEEDLAANDILDYKDDDDKV |
| Purity | > 80% as determined by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie blue staining |
| Concentration | >0.05 µg/µL as determined by microplate BCA method |
| Labeling Method | Labeled with [U- 13C6, 15N4]-L-Arginine and [U- 13C6, 15N2]-L-Lysine |
| Buffer | 25 mM Tris-HCl, 100 mM glycine, pH 7.3 |
| Storage | Store at -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Stability | Stable for 3 months from receipt of products under proper storage and handling conditions. |
| Reference Data | |
| RefSeq | NP_002727 |
| RefSeq Size | 3678 |
| RefSeq ORF | 1254 |
| Synonyms | PRKAR2; RII-BETA |
| Locus ID | 5577 |
| UniProt ID | P31323, A0A024R712, B3KY43 |
| Cytogenetics | 7q22.3 |
| Summary | cAMP is a signaling molecule important for a variety of cellular functions. cAMP exerts its effects by activating the cAMP-dependent protein kinase, which transduces the signal through phosphorylation of different target proteins. The inactive kinase holoenzyme is a tetramer composed of two regulatory and two catalytic subunits. cAMP causes the dissociation of the inactive holoenzyme into a dimer of regulatory subunits bound to four cAMP and two free monomeric catalytic subunits. Four different regulatory subunits and three catalytic subunits have been identified in humans. The protein encoded by this gene is one of the regulatory subunits. This subunit can be phosphorylated by the activated catalytic subunit. This subunit has been shown to interact with and suppress the transcriptional activity of the cAMP responsive element binding protein 1 (CREB1) in activated T cells. Knockout studies in mice suggest that this subunit may play an important role in regulating energy balance and adiposity. The studies also suggest that this subunit may mediate the gene induction and cataleptic behavior induced by haloperidol. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| Protein Families | Druggable Genome |
| Protein Pathways | Apoptosis, Insulin signaling pathway |
Documents
| FAQs |
| SDS |
Resources
Recombinant Protein Resources |
Other Versions
| SKU | Description | Size | Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| LC419138 | PRKAR2B HEK293T cell transient overexpression lysate (as WB positive control) |
USD 134.00 |
|
| LY419138 | Transient overexpression lysate of protein kinase, cAMP-dependent, regulatory, type II, beta (PRKAR2B) |
USD 436.00 |
|
| TP309900 | Recombinant protein of human protein kinase, cAMP-dependent, regulatory, type II, beta (PRKAR2B), 20 µg |
USD 867.00 |
{0} Product Review(s)
Be the first one to submit a review






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China