Bromodeoxyuridine / BrDU Mouse Monoclonal Antibody [Clone ID: SPM537]
CAT#: AM33288PU-T
Bromodeoxyuridine / BrDU mouse monoclonal antibody, clone SPM537, Purified
Size: 100 ug
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Clone Name | SPM537 |
| Applications | FC, IF, IHC |
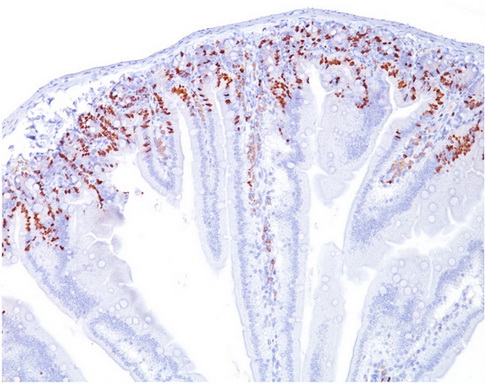
| Recommended Dilution | Flow Cytometry: 0.5-1 µg/106 cells. Immunofluorescence: 0.5-1 µg/ml. Immunohistochemistry on Frozen and Formalin-Fixed Sections: 0.5-1 µg/ml for 30 minutes at RT. For staining of formalin-fixed tissues, incubate sections in 4N HCl for 30 minutes at RT followed by digestion with trypsin at 1mg/ml PBS, 10 min at 37°C. Recommended Positive Control: Cells grown in presence of BrdU or tissues from experimental animals injected with BrdU. |
| Reactivities | All Species |
| Host | Mouse |
| Isotype | IgG1 |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Immunogen | Bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU) conjugated to KLH |
| Specificity | It reacts with Bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU) in single stranded DNA (produced by partial denaturation of double stranded DNA), BrdU coupled to a protein carrier, as well as free BrdU. BrdU is a thymidine analog, incorporated into cell nuclei during DNA synthesis prior to mitosis. Antibody to BrdU is helpful in detecting S-phase cells, providing useful information on the aggressiveness of tumors. Cellular Localization: Nuclear. |
| Formulation | 10mM PBS State: Purified State: Liquid purified IgG fraction from Bioreactor Concentrate Stabilizer: 0.05% BSA Preservative: 0.05% Sodium Azide |
| Concentration | lot specific |
| Purification | Protein A/G Chromatography |
| Conjugation | Unconjugated |
| Storage | Store undiluted at 2-8°C. DO NOT FREEZE! |
| Stability | Shelf life: one year from despatch. |
| Predicted Protein Size | Depends on the target |
| Background | Bromodexyuridine (BrdU) is a thymidine analog which is selectively incorporated into the DNA of proliferating cells to provide a marker for the DNA being replicated. The number of proliferating cells can then be detected in cell lysates, tissue sections or suspensions using an antibody specific for the BrdU. Previous methods of detecting DNA included the use of [3H]-thymidine which would be incorporated into the DNA and could then the DNA could be quantified by autoradiography or scintillation counting. These methods are more difficult and require more cleanup due to the radioactive material. An immunohistochemical assay provides a much simpler and cleaner method for detecting DNA in cells. |
| Reference Data | |
Documents
| Product Manuals |
| FAQs |
| SDS |
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China