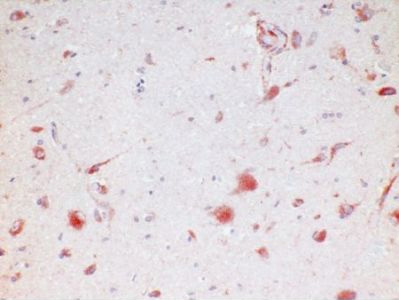
Huntingtin (HTT) (1247-1646) Mouse Monoclonal Antibody [Clone ID: 3HU-4E6]
CAT#: AM26742PU-N
Huntingtin (HTT) (1247-1646) mouse monoclonal antibody, clone 3HU-4E6, Purified
Other products for "HTT"
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Clone Name | 3HU-4E6 |
| Applications | IHC |
| Recommended Dilution | Immunohistochemistry on Paraffin Sections: 2 µg/ml (1/100). Microwave pretreatment in citrate buffer is recommended for antigen retrieval. Suggested Positive Control: Human hypothalamus. |
| Reactivities | Human, Mouse |
| Host | Mouse |
| Isotype | IgG2b |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Immunogen | Recombinant Huntingtin fragment amino acids 1247 to 1646 |
| Specificity | This antibody detects Huntingtin at aa 1247-1646. Antigen Distribution: Nucleus but also cytoplasmic expression in most tissues. Highest levels in neurons and paneth cells in gastrointestinal tract. Distinct granular expression pattern in several glandular epithelia |
| Formulation | PBS, pH 7.2 State: Purified State: Lyophilized purified Ig fraction Stabilizer: 5 mg/ml BSA Preservative: 0.01% Kathon |
| Reconstitution Method | Restore by adding 0.5 ml distilled water. |
| Concentration | 0.2 mg/ml IgG (after reconstitution) |
| Purification | Affinity Chromatography |
| Conjugation | Unconjugated |
| Storage | Store lyophilized at 2-8°C for 6 months or at -20°C long term. After reconstitution store the antibody undiluted at 2-8°C for one month or (in aliquots) at -20°C long term. Avoid repeated freezing and thawing. |
| Stability | Shelf life: one year from despatch. |
| Gene Name | huntingtin |
| Database Link | |
| Background | Huntingtin is a disease gene linked to Huntington's disease, a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by loss of striatal neurons. This is thought to be caused by an expanded, unstable trinucleotide repeat in the huntingtin gene, which trans lates as a polyglutamine repeat in the protein product. A fairly broad range in the number of trinucleotide repeats has been identified in normal controls, and repeat numbers in excess of 40 have been described as pathological. The huntingtin locus is large, spanning 180 kb and consisting of 67 exons. The huntingtin gene is widely expressed and is required for normal development. It is expressed as 2 alternatively polyadenylated forms displaying different relative abundance in various fetal and adult tissues. The larger transcript is approximately 13.7 kb and is expressed predominantly in adult and fetal brain whereas the smaller transcript of approximately 10.3 kb is more widely expressed. The genetic defect leading to Huntington's disease may not necessarily eliminate transcription, but may confer a new property on the mRNA or alter the function of the protein. One candidate is the huntingtin-associated protein-1, highly expressed in brain, which has increased affinity for huntingtin protein with expanded p olyglutamine repeats. This gene contains an upstream open reading frame in the 5' UTR that inhibits expression of the huntingtin gene product through translational repression. [provided by RefSeq] Antigen distribution: Nucleus but also cytoplasmic expression in most tissues. Highest levels in neurons and paneth cells in gastrointestinal tract. Distinct granular expression pattern in several glandular epithelia. |
| Synonyms | Huntington Disease Protein, HD, IT15, HTT |
| Reference Data | |
Documents
| Product Manuals |
| FAQs |
| SDS |
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China