Tubulin (TUBA1B) (N-term) Mouse Monoclonal Antibody [Clone ID: TU-02]
CAT#: AM03088PU-N
Tubulin (TUBA1B) (N-term) mouse monoclonal antibody, clone TU-02, Purified
Other products for "Tubulin"
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Clone Name | TU-02 |
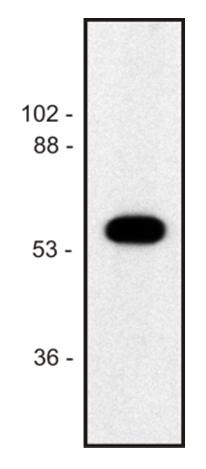
| Applications | WB |
| Recommended Dilution | Western Blot (Reducing conditions): 1-2 μg/ml Positive control: porcine brain lysate. Sample preparation: Mix lysate with reducing Laemmli SDS-PAGE sample buffer. |
| Reactivities | Human, Mouse, Porcine |
| Host | Mouse |
| Isotype | IgM |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Immunogen | Microtubule proteins from porcine brain |
| Specificity | The antibody TU-02 recognizes an epitope on N-terminal structural domain of alpha-tubulin. |
| Formulation | Tris buffered saline (TBS) with 15 mM sodium azide, approx. pH 8.0 State: Purified State: Liquid purified IgG fraction (> 95% pure by SDS-PAGE) |
| Concentration | lot specific |
| Purification | Precipitation methods |
| Conjugation | Unconjugated |
| Storage | Store undiluted at 2-8°C. DO NOT FREEZE! |
| Stability | Shelf life: one year from despatch. |
| Gene Name | tubulin alpha 1b |
| Database Link | |
| Background | The microtubules are intracellular dynamic polymers made up of evolutionarily conserved polymorphic alpha/beta-tubulin heterodimers and a large number of microtubule-associated proteins (MAPs). The microtubules consist of 13 protofilaments and have an outer diameter 25 nm. Microtubules have their intrinsic polarity; highly dynamic plus ends and less dynamic minus ends. Microtubules are required for vital processes in eukaryotic cells including mitosis, meiosis, maintenance of cell shape and intracellular transport. Microtubules are also necessary for movement of cells by means of flagella and cilia. In mammalian tissue culture cells microtubules have their minus ends anchored in microtubule organizing centers (MTOCs).The GTP (guanosintriphosphate) molecule is an essential for tubulin heterodimer to associate with other heterodimers to form microtubule. In vivo, microtubule dynamics vary considerably. Microtubule polymerization is reversible and a populations of microtubules in cells are on their minus ends either growing or shortening - this phenomenon is called dynamic instability of microtubules. On a practical level, microtubules can easily be stabilized by the addition of non-hydrolysable analogues of GTP (eg. GMPPCP) or more commonly by anti-cancer drugs such as Taxol. Taxol stabilizes microtubules at room temperature for many hours. Using limited proteolysis by enzymes both tubulin subunits can be divided into N-terminal and C-terminal structural domains. The alpha-tubulin (relative molecular weight about 50 kDa) is globular protein that exists in cells as part of soluble alpha/beta-tubulin dimer or it is polymerized into microtubules. In different species it is coded by multiple tubulin genes that form tubulin classes (in human 6 genes). Expressed tubulin genes are named tubulin isotypes. Some of the tubulin isotypes are expressed ubiquitously, while some have more restricted tissue expression. Alpha-tubulin is also subject of numerous post-translational modifications. Tubulin isotypes and their posttranslational modifications are responsible for multiple tubulin charge variants - tubulin isoforms. Heterogeneity of alpha-tubulin is concentrated in C-terminal structural domain. |
| Synonyms | Tubulin alpha-1B chain, Tubulin alpha-ubiquitous chain, Alpha-tubulin ubiquitous, Tubulin K-alpha-1 |
| Reference Data | |
| Protein Families | Druggable Genome |
| Protein Pathways | Gap junction, Pathogenic Escherichia coli infection |
Documents
| Product Manuals |
| FAQs |
| SDS |
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China