KCNQ1 (NM_181798) Human Recombinant Protein
CAT#: TP762235
Purified recombinant protein of Human potassium voltage-gated channel, KQT-like subfamily, member 1 (KCNQ1), transcript variant 2, Ala257-End, with N-terminal His tag, expressed in E.coli, 50ug
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Species | Human |
| Expression Host | E. coli |
| Expression cDNA Clone or AA Sequence |
A DNA sequence encoding the region(Ala257-End) of KCNQ1
|
| Tag | N-His |
| Predicted MW | 32.9 kDa |
| Concentration | >0.05 µg/µL as determined by microplate BCA method |
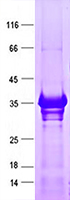
| Purity | > 80% as determined by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie blue staining |
| Buffer | 50 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.0, 8 M urea |
| Note | For testing in cell culture applications, please filter before use. Note that you may experience some loss of protein during the filtration process. |
| Storage | Store at -80°C. |
| Stability | Stable for 12 months from the date of receipt of the product under proper storage and handling conditions. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Reference Data | |
| RefSeq | NP_861463 |
| Locus ID | 3784 |
| UniProt ID | P51787 |
| Cytogenetics | 11p15.5-p15.4 |
| Refseq Size | 3029 |
| Refseq ORF | 1647 |
| Synonyms | ATFB1; ATFB3; JLNS1; KCNA8; KCNA9; Kv1.9; Kv7.1; KVLQT1; LQT; LQT1; RWS; SQT2; WRS |
| Summary | This gene encodes a voltage-gated potassium channel required for repolarization phase of the cardiac action potential. This protein can form heteromultimers with two other potassium channel proteins, KCNE1 and KCNE3. Mutations in this gene are associated with hereditary long QT syndrome 1 (also known as Romano-Ward syndrome), Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome, and familial atrial fibrillation. This gene exhibits tissue-specific imprinting, with preferential expression from the maternal allele in some tissues, and biallelic expression in others. This gene is located in a region of chromosome 11 amongst other imprinted genes that are associated with Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome (BWS), and itself has been shown to be disrupted by chromosomal rearrangements in patients with BWS. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2011] |
| Protein Families | Druggable Genome, Ion Channels: Potassium, Transmembrane |
| Protein Pathways | Vibrio cholerae infection |
Documents
| FAQs |
| SDS |
Resources
Recombinant Protein Resources |
Other Versions
| SKU | Description | Size | Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| LC405589 | KCNQ1 HEK293T cell transient overexpression lysate (as WB positive control) |
USD 206.00 |
|
| LC424853 | KCNQ1 HEK293T cell transient overexpression lysate (as WB positive control) |
USD 206.00 |
|
| LC424989 | KCNQ1 HEK293T cell transient overexpression lysate (as WB positive control) |
USD 206.00 |
|
| LY405589 | Transient overexpression lysate of potassium voltage-gated channel, KQT-like subfamily, member 1 (KCNQ1), transcript variant 2 |
USD 665.00 |
|
| LY424853 | Transient overexpression lysate of potassium voltage-gated channel, KQT-like subfamily, member 1 (KCNQ1), transcript variant 1 |
USD 665.00 |
{0} Product Review(s)
Be the first one to submit a review






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China