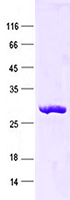
Cyclin E1 (CCNE1) (NM_001238) Human Recombinant Protein
CAT#: TP762098
Purified recombinant protein of Human cyclin E1 (CCNE1), transcript variant 1,Ile96-Ala378, with N-terminal His tag, expressed in E. coli, 50ug
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Species | Human |
| Expression Host | E. coli |
| Expression cDNA Clone or AA Sequence |
A DNA sequence encoding the region(Ile96-Ala378) of CCNE1
|
| Tag | N-His |
| Predicted MW | 32.9 kDa |
| Concentration | >0.05 µg/µL as determined by microplate BCA method |
| Purity | > 80% as determined by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie blue staining |
| Buffer | 50 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.0, 8 M urea |
| Note | For testing in cell culture applications, please filter before use. Note that you may experience some loss of protein during the filtration process. |
| Storage | Store at -80°C. |
| Stability | Stable for 12 months from the date of receipt of the product under proper storage and handling conditions. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Reference Data | |
| RefSeq | NP_001229 |
| Locus ID | 898 |
| UniProt ID | P24864 |
| Cytogenetics | 19q12 |
| Refseq Size | 2021 |
| Refseq ORF | 1230 |
| Synonyms | CCNE; pCCNE1 |
| Summary | The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the highly conserved cyclin family, whose members are characterized by a dramatic periodicity in protein abundance through the cell cycle. Cyclins function as regulators of CDK kinases. Different cyclins exhibit distinct expression and degradation patterns which contribute to the temporal coordination of each mitotic event. This cyclin forms a complex with and functions as a regulatory subunit of CDK2, whose activity is required for cell cycle G1/S transition. This protein accumulates at the G1-S phase boundary and is degraded as cells progress through S phase. Overexpression of this gene has been observed in many tumors, which results in chromosome instability, and thus may contribute to tumorigenesis. This protein was found to associate with, and be involved in, the phosphorylation of NPAT protein (nuclear protein mapped to the ATM locus), which participates in cell-cycle regulated histone gene expression and plays a critical role in promoting cell-cycle progression in the absence of pRB. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2016] |
| Protein Families | Druggable Genome, Stem cell - Pluripotency, Stem cell relevant signaling - DSL/Notch pathway, Transcription Factors |
| Protein Pathways | Cell cycle, Oocyte meiosis, p53 signaling pathway, Pathways in cancer, Prostate cancer, Small cell lung cancer |
Documents
| FAQs |
| SDS |
Resources
Recombinant Protein Resources |
Other Versions
| SKU | Description | Size | Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| LC400495 | CCNE1 HEK293T cell transient overexpression lysate (as WB positive control) |
USD 134.00 |
|
| LY400495 | Transient overexpression lysate of cyclin E1 (CCNE1), transcript variant 1 |
USD 436.00 |
|
| TP304289 | Purified recombinant protein of Human cyclin E1 (CCNE1), transcript variant 1, 20 µg |
USD 867.00 |
{0} Product Review(s)
Be the first one to submit a review






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China