gldA (1-367, His-tag) Escherichia coli Protein
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Species | Escherichia coli |
| Expression Host | E. coli |
| Expression cDNA Clone or AA Sequence |
MGSSHHHHHH SSGLVPRGSH MGSMDRIIQS PGKYIQGADV INRLGEYLKP LAERWLVVGD KFVLGFAQST VEKSFKDAGL VVEIAPFGGE CSQNEIDRLR GIAETAQCGA ILGIGGGKTL DTAKALAHFM GVPVAIAPTI ASTDAPCSAL SVIYTDEGEF DRYLLLPNNP NMVIVDTKIV AGAPARLLAA GIGDALATWF EARACSRSGA TTMAGGKCTQ AALALAELCY NTLLEEGEKA MLAAEQHVVT PALERVIEAN TYLSGVGFES GGLAAAHAVH NGLTAIPDAH HYYHGEKVAF GTLTQLVLEN APVEEIETVA ALSHAVGLPI TLAQLDIKED VPAKMRIVAE AACAEGETIH NMPGGATPDQ VYAALLVADQ YGQRFLQEWE
|
| Tag | His-tag |
| Predicted MW | 41.1 kDa |
| Concentration | lot specific |
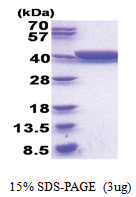
| Purity | >95% by SDS - PAGE |
| Presentation | Purified |
| Buffer | Presentation State: Purified State: Liquid purified protein Buffer System: Phosphate buffered saline (pH 7.4), 10% glycerol |
| Bioactivity | Specific: > 14 Units/ml One unit will oxidize 1.0 umole of glycerol to dihydroxyacetone per minute at pH 8.0 at 25C |
| Preparation | Liquid purified protein |
| Applications | Protocol: 1. Prepare a 200ul reaction mix into a suitable container: The final concentrations are 93mM Glycine, 93mM Potassium chloride, 2375mM Glycerol, 3mM b-NAD. 2. Equilibrate to 25C and monitor at A340nm until the value is constant using a spectrophotometer. 3. Add 20ul of recombinant gldA protein with various concentrations (0.2ug, 0.1ug, 0.05ug) in 180ul reaction buffer. 4. Mix by inversion and record the decrease at A340nm for 10 minutes. |
| Protein Description | Recombinant E. coli gldA protein, fused to His-tag at N-terminus, was expressed in E.coli and purified by using conventional chromatography techniques. |
| Storage | Store undiluted at 2-8°C for one week or (in aliquots) at -20°C to -80°C for longer. Avoid repeated freezing and thawing. |
| Stability | Shelf life: one year from despatch. |
| Reference Data | |
| Summary | gldA catalyzes the NAD-dependent oxidation of glycerol to dihydroxyacetone (glycerone). This protein allows microorganisms to utilize glycerol as a source of carbon under anaerobic conditions. In E.coli, an important role of GldA is also likely to regulate the intracellular level of dihydroxyacetone by catalyzing the reverse reaction, i.e. the conversion of dihydroxyacetone into glycerol. gldA possesses a broad substrate specificity, since it is also able to oxidize 1,2-propanediol and to reduce glycolaldehyde, methylglyoxal and hydroxyacetone into ethylene glycol, lactaldehyde and 1,2-propanediol, respectively. |
Documents
| FAQs |
| SDS |
Resources
Recombinant Protein Resources |
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China