CDK5 (1-292, His-tag) Human Protein
Other products for "CDK5"
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Species | Human |
| Expression Host | E. coli |
| Expression cDNA Clone or AA Sequence |
MGSSHHHHHH SSGLVPRGSH MGSHMQKYEK LEKIGEGTYG TVFKAKNRET HEIVALKRVR LDDDDEGVPS SALREICLLK ELKHKNIVRL HDVLHSDKKL TLVFEFCDQD LKKYFDSCNG DLDPEIVKSF LFQLLKGLGF CHSRNVLHRD LKPQNLLINR NGELKLADFG LARAFGIPVR CYSAEVVTLW YRPPDVLFGA KLYSTSIDMW SAGCIFAELA NAGRPLFPGN DVDDQLKRIF RLLGTPTEEQ WPSMTKLPDY KPYPMYPATT SLVNVVPKLN ATGRDLLQNL LKCNPVQRIS AEEALQHPYF SDFCPP
|
| Tag | His-tag |
| Predicted MW | 35.8 kDa |
| Concentration | lot specific |
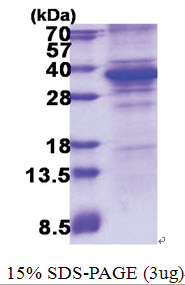
| Purity | >85% by SDS - PAGE |
| Presentation | Purified |
| Buffer | Presentation State: Purified State: Liquid purified protein Buffer System: 20 mM Tris-HCl buffer (pH 8.0) containing 10% glycerol 0.4M Urea |
| Preparation | Liquid purified protein |
| Protein Description | Recombinant human CDK5 protein, fused to His-tag at N-terminus, was expressed in E.coli. |
| Storage | Store undiluted at 2-8°C for one week or (in aliquots) at -20°C to -80°C for longer. Avoid repeated freezing and thawing. |
| Stability | Shelf life: one year from despatch. |
| Reference Data | |
| RefSeq | NP_001157882 |
| Locus ID | 1020 |
| UniProt ID | Q00535, A0A0S2Z355 |
| Cytogenetics | 7q36.1 |
| Synonyms | LIS7; PSSALRE |
| Summary | This gene encodes a proline-directed serine/threonine kinase that is a member of the cyclin-dependent kinase family of proteins. Unlike other members of the family, the protein encoded by this gene does not directly control cell cycle regulation. Instead the protein, which is predominantly expressed at high levels in mammalian postmitotic central nervous system neurons, functions in diverse processes such as synaptic plasticity and neuronal migration through phosphorylation of proteins required for cytoskeletal organization, endocytosis and exocytosis, and apoptosis. In humans, an allelic variant of the gene that results in undetectable levels of the protein has been associated with lethal autosomal recessive lissencephaly-7. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, May 2015] |
| Protein Families | Druggable Genome, Protein Kinase |
| Protein Pathways | Alzheimer's disease, Axon guidance |
Documents
| FAQs |
| SDS |
Resources
Recombinant Protein Resources |
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China