Bcl-10 (1-233, His-tag) Human Protein
Other products for "BCL10"
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Species | Human |
| Expression Host | E. coli |
| Expression cDNA Clone or AA Sequence |
MGSSHHHHHH SSGLVPRGSH MGSHMEPTAP SLTEEDLTEV KKDALENLRV YLCEKIIAER HFDHLRAKKI LSREDTEEIS CRTSSRKRAG KLLDYLQENP KGLDTLVESI RREKTQNFLI QKITDEVLKL RNIKLEHLKG LKCSSCEPFP DGATNNLSRS NSDESNFSEK LRASTVMYHP EGESSTTPFF STNSSLNLPV LEVGRTENTI FSSTTLPRPG DPGAPPLPPD LQLEEEGTCA NSSEMFLPLR SRTVSRQ
|
| Tag | His-tag |
| Predicted MW | 28.8 kDa |
| Concentration | lot specific |
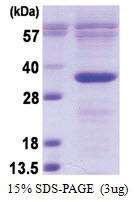
| Purity | >85% by SDS - PAGE |
| Presentation | Purified |
| Buffer | Presentation State: Purified State: Liquid purified protein Buffer System: 20 mM Tris-HCl buffer (pH 8.0) containing 10% glycerol, 0.05M NaCl, 1 mM DTT |
| Preparation | Liquid purified protein |
| Protein Description | Recombinant human BCL10 protein, fused to His-tag at N-terminus, was expressed in E.coli and purified by using conventional chromatography. |
| Storage | Store undiluted at 2-8°C for one week or (in aliquots) at -20°C to -80°C for longer. Avoid repeated freezing and thawing. |
| Stability | Shelf life: one year from despatch. |
| Reference Data | |
| RefSeq | NP_001307644 |
| Locus ID | 8915 |
| UniProt ID | A0A087WWW9, A2TDT2 |
| Cytogenetics | 1p22.3 |
| Synonyms | c-E10; CARMEN; CIPER; CLAP; IMD37; mE10 |
| Summary | This gene was identified by its translocation in a case of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) lymphoma. The protein encoded by this gene contains a caspase recruitment domain (CARD), and has been shown to induce apoptosis and to activate NF-kappaB. This protein is reported to interact with other CARD domain containing proteins including CARD9, 10, 11 and 14, which are thought to function as upstream regulators in NF-kappaB signaling. This protein is found to form a complex with MALT1, a protein encoded by another gene known to be translocated in MALT lymphoma. MALT1 and this protein are thought to synergize in the activation of NF-kappaB, and the deregulation of either of them may contribute to the same pathogenetic process that leads to the malignancy. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2016] |
| Protein Families | Druggable Genome |
| Protein Pathways | B cell receptor signaling pathway, T cell receptor signaling pathway |
Documents
| FAQs |
| SDS |
Resources
Recombinant Protein Resources |
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China