CD254 / RANKL (140-317, His-tag) Human Protein
Other products for "TNFSF11"
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Species | Human |
| Expression Host | E. coli |
| Expression cDNA Clone or AA Sequence |
MGSSHHHHHH SSGLVPRGSH MIRAEKAMVD GSWLDLAKRS KLEAQPFAHL TINATDIPSG SHKVSLSSWY HDRGWAKISN MTFSNGKLIV NQDGFYYLYA NICFRHHETS GDLATEYLQL MVYVTKTSIK IPSSHTLMKG GSTKYWSGNS EFHFYSINVG GFFKLRSGEE ISIEVSNPSL LDPDQDATYF GAFKVRDID
|
| Tag | His-tag |
| Predicted MW | 22.3 kDa |
| Concentration | lot specific |
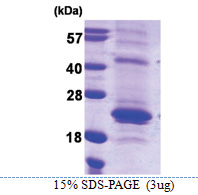
| Purity | >80% |
| Presentation | Purified |
| Buffer | Presentation State: Purified State: Liquid purified protein Buffer System: 20 mM Tris-HCl buffer (pH 8.0) containing 20% glycerol, 0.1M NaCl, 1 mM DTT |
| Preparation | Liquid purified protein |
| Protein Description | Recombinant human RANKL protein, fused to His-tag at N-terminus, was expressed in E.coli and purified by using conventional chromatography. |
| Storage | Store undiluted at 2-8°C for up to two weeks or (in aliquots) at -20°C or -70°C for longer. Avoid repeated freezing and thawing. |
| Stability | Shelf life: one year from despatch. |
| Reference Data | |
| RefSeq | NP_003692 |
| Locus ID | 8600 |
| UniProt ID | O14788, Q5T9Y4 |
| Cytogenetics | 13q14.11 |
| Synonyms | CD254; hRANKL2; ODF; OPGL; OPTB2; RANKL; sOdf; TNLG6B; TRANCE |
| Summary | This gene encodes a member of the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) cytokine family which is a ligand for osteoprotegerin and functions as a key factor for osteoclast differentiation and activation. This protein was shown to be a dentritic cell survival factor and is involved in the regulation of T cell-dependent immune response. T cell activation was reported to induce expression of this gene and lead to an increase of osteoclastogenesis and bone loss. This protein was shown to activate antiapoptotic kinase AKT/PKB through a signaling complex involving SRC kinase and tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor (TRAF) 6, which indicated this protein may have a role in the regulation of cell apoptosis. Targeted disruption of the related gene in mice led to severe osteopetrosis and a lack of osteoclasts. The deficient mice exhibited defects in early differentiation of T and B lymphocytes, and failed to form lobulo-alveolar mammary structures during pregnancy. Two alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| Protein Families | Druggable Genome, Transmembrane |
| Protein Pathways | Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction |
Documents
| FAQs |
| SDS |
Resources
Recombinant Protein Resources |
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China