AUH (68-339, His-tag) Human Protein
Other products for "AUH"
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Species | Human |
| Expression Host | E. coli |
| Expression cDNA Clone or AA Sequence |
MGSSHHHHHH SSGLVPRGSH MSSEMKTEDE LRVRHLEEEN RGIVVLGINR AYGKNSLSKN LIKMLSKAVD ALKSDKKVRT IIIRSEVPGI FCAGADLKER AKMSSSEVGP FVSKIRAVIN DIANLPVPTI AAIDGLALGG GLELALACDI RVAASSAKMG LVETKLAIIP GGGGTQRLPR AIGMSLAKEL IFSARVLDGK EAKAVGLISH VLEQNQEGDA AYRKALDLAR EFLPQGPVAM RVAKLAINQG MEVDLVTGLA IEEACYAQTI PTKDRLEGLL AFKEKRPPRY KGE
|
| Tag | His-tag |
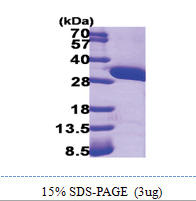
| Predicted MW | 31.4 kDa |
| Concentration | lot specific |
| Purity | >95% |
| Presentation | Purified |
| Buffer | Presentation State: Purified State: Liquid purified protein Buffer System: 20 mM Tris-HCl buffer (pH 8.0) containing 20% glycerol, 0.1M NaCl, 1 mM DTT |
| Preparation | Liquid purified protein |
| Protein Description | Recombinant human AUH protein, fused to His-tag at N-terminus, was expressed in E.coli and purified by using conventional chromatography. |
| Storage | Store undiluted at 2-8°C for up to two weeks or (in aliquots) at -20°C or -70°C for longer. Avoid repeated freezing and thawing. |
| Stability | Shelf life: one year from despatch. |
| Reference Data | |
| RefSeq | NP_001293119 |
| Locus ID | 549 |
| UniProt ID | Q13825, Q13825-2 |
| Cytogenetics | 9q22.31 |
| Summary | This gene encodes bifunctional mitochondrial protein that has both RNA-binding and hydratase activities. The encoded protein is a methylglutaconyl-CoA hydratase that catalyzes the hydration of 3-methylglutaconyl-CoA to 3-hydroxy-3-methyl-glutaryl-CoA, a critical step in the leucine degradation pathway. This protein also binds AU-rich elements (AREs) found in the 3' UTRs of rapidly decaying mRNAs including c-fos, c-myc and granulocyte/ macrophage colony stimulating factor. ARE elements are involved in directing RNA to rapid degradation and deadenylation. This protein is localizes to the mitochondrial matrix and the inner mitochondrial membrane and may be involved in mitochondrial protein synthesis. Mutations in this gene are the cause of 3-methylglutaconic aciduria, type I. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2015] |
| Protein Pathways | Metabolic pathways, Valine, leucine and isoleucine degradation |
Documents
| FAQs |
| SDS |
Resources
Recombinant Protein Resources |
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China