alpha A Crystallin (CRYAA) (NM_000394) Human Mass Spec Standard
CAT#: PH316946
CRYAA MS Standard C13 and N15-labeled recombinant protein (NP_000385)
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Tag | C-Myc/DDK |
| Species | Human |
| Expression Host | HEK293 |
| Expression cDNA Clone or AA Sequence | RC216946 |
| Predicted MW | 19.9 kDa |
| Protein Sequence |
>RC216946 protein sequence
Red=Cloning site Green=Tags(s) MDVTIQHPWFKRTLGPFYPSRLFDQFFGEGLFEYDLLPFLSSTISPYYRQSLFRTVLDSGISEVRSDRDK FVIFLDVKHFSPEDLTVKVQDDFVEIHGKHNERQDDHGYISREFHRRYRLPSNVDQSALSCSLSADGMLT FCGPKIQTGLDATHAERAIPVSREEKPTSAPSS TRTRPLEQKLISEEDLAANDILDYKDDDDKV |
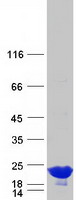
| Purity | > 80% as determined by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie blue staining |
| Concentration | >0.05 µg/µL as determined by microplate BCA method |
| Labeling Method | Labeled with [U- 13C6, 15N4]-L-Arginine and [U- 13C6, 15N2]-L-Lysine |
| Buffer | 25 mM Tris-HCl, 100 mM glycine, pH 7.3 |
| Storage | Store at -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Stability | Stable for 3 months from receipt of products under proper storage and handling conditions. |
| Reference Data | |
| RefSeq | NP_000385 |
| RefSeq Size | 1162 |
| RefSeq ORF | 519 |
| Synonyms | CRYA1; CTRCT9; HSPB4 |
| Locus ID | 1409 |
| UniProt ID | P02489, A0A140G945 |
| Cytogenetics | 21q22.3 |
| Summary | Mammalian lens crystallins are divided into alpha, beta, and gamma families. Alpha crystallins are composed of two gene products: alpha-A and alpha-B, for acidic and basic, respectively. Alpha crystallins can be induced by heat shock and are members of the small heat shock protein (HSP20) family. They act as molecular chaperones although they do not renature proteins and release them in the fashion of a true chaperone; instead they hold them in large soluble aggregates. Post-translational modifications decrease the ability to chaperone. These heterogeneous aggregates consist of 30-40 subunits; the alpha-A and alpha-B subunits have a 3:1 ratio, respectively. Two additional functions of alpha crystallins are an autokinase activity and participation in the intracellular architecture. The encoded protein has been identified as a moonlighting protein based on its ability to perform mechanistically distinct functions. Alpha-A and alpha-B gene products are differentially expressed; alpha-A is preferentially restricted to the lens and alpha-B is expressed widely in many tissues and organs. Defects in this gene cause autosomal dominant congenital cataract (ADCC). [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2014] |
Documents
| FAQs |
| SDS |
Resources
Recombinant Protein Resources |
Other Versions
| SKU | Description | Size | Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| LC424743 | CRYAA HEK293T cell transient overexpression lysate (as WB positive control) |
USD 134.00 |
|
| LY424743 | Transient overexpression lysate of crystallin, alpha A (CRYAA) |
USD 436.00 |
|
| TP316946 | Recombinant protein of human crystallin, alpha A (CRYAA), 20 µg |
USD 867.00 |
|
| TP720865 | Purified recombinant protein of Human crystallin, alpha A (CRYAA) |
USD 330.00 |
{0} Product Review(s)
Be the first one to submit a review






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China