Sting1 Mouse Gene Knockout Kit (CRISPR)
CAT#: KN317757BN
Tmem173 - mouse gene knockout kit via CRISPR, HDR mediated
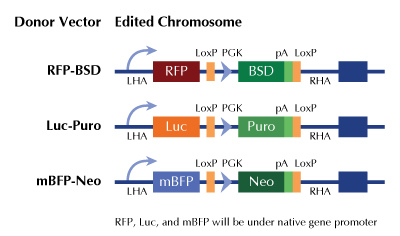
Functional Cassette: GFP-puro Luciferase-Puro RFP-BSD
HDR-mediated knockout kit validation
USD 1,657.00
4 Weeks*
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Format | 2 gRNA vectors, 1 mBFP-Neo donor, 1 scramble control |
| Donor DNA | mBFP-Neo |
| Symbol | Sting1 |
| Locus ID | 72512 |
| Components |
KN317757G1, Sting1 gRNA vector 1 in pCas-Guide CRISPR vector KN317757G2, Sting1 gRNA vector 2 in pCas-Guide CRISPR vector KN317757BND, donor DNA containing left and right homologous arms and mBFP-Neo functional cassette. GE100003, scramble sequence in pCas-Guide vector |
| Disclaimer | These products are manufactured and supplied by OriGene under license from ERS. The kit is designed based on the best knowledge of CRISPR technology. The system has been functionally validated for knocking-in the cassette downstream the native promoter. The efficiency of the knock-out varies due to the nature of the biology and the complexity of the experimental process. |
| Reference Data | |
| RefSeq | NM_001289591, NM_001289592, NM_028261 |
| UniProt ID | Q3TBT3 |
| Synonyms | 2610307O08Rik; ERIS; Mita; MPYS; STING |
| Summary | Facilitator of innate immune signaling that acts as a sensor of cytosolic DNA from bacteria and viruses and promotes the production of type I interferon (IFN-alpha and IFN-beta) (PubMed:18818105, PubMed:19433799, PubMed:19776740, PubMed:26229117, PubMed:26669264). Innate immune response is triggered in response to non-CpG double-stranded DNA from viruses and bacteria delivered to the cytoplasm (PubMed:18818105, PubMed:19433799, PubMed:19776740, PubMed:26229117, PubMed:26669264). Acts by binding cyclic dinucleotides: recognizes and binds cyclic di-GMP (c-di-GMP), a second messenger produced by bacteria, and cyclic GMP-AMP (cGAMP), a messenger produced by CGAS in response to DNA virus in the cytosol (PubMed:21947006, PubMed:23722158, PubMed:23258412, PubMed:23519410, PubMed:23910378). Upon binding of c-di-GMP or cGAMP, TMEM173/STING oligomerizes, translocates from the endoplasmic reticulum and is phosphorylated by TBK1 on the pLxIS motif, leading to recruitment and subsequent activation of the transcription factor IRF3 to induce expression of type I interferon and exert a potent anti-viral state (PubMed:25636800). In addition to promote the production of type I interferons, plays a direct role in autophagy (PubMed:30568238). Following cGAMP-binding, TMEM173/STING buds from the endoplasmic reticulum into COPII vesicles, which then form the endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment (ERGIC) (By similarity). The ERGIC serves as the membrane source for WIPI2 recruitment and LC3 lipidation, leading to formation of autophagosomes that target cytosolic DNA or DNA viruses for degradation by the lysosome (By similarity). The autophagy- and interferon-inducing activities can be uncoupled and autophagy induction is independent of TBK1 phosphorylation (By similarity). Autophagy is also triggered upon infection by bacteria: following c-di-GMP-binding, which is produced by live Gram-positive bacteria, promotes reticulophagy (PubMed:29056340). Exhibits 2',3' phosphodiester linkage-specific ligand recognition: can bind both 2'-3' linked cGAMP (2'-3'-cGAMP) and 3'-3' linked cGAMP but is preferentially activated by 2'-3' linked cGAMP (PubMed:26300263). The preference for 2'-3'-cGAMP, compared to other linkage isomers is probably due to the ligand itself, whichs adopts an organized free-ligand conformation that resembles the TMEM173/STING-bound conformation and pays low energy costs in changing into the active conformation (By similarity). May be involved in translocon function, the translocon possibly being able to influence the induction of type I interferons (By similarity). May be involved in transduction of apoptotic signals via its association with the major histocompatibility complex class II (MHC-II) (PubMed:18559423).[UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot Function] |
Documents
| Product Manuals |
| FAQs |
| SDS |
Resources
Other Versions
| SKU | Description | Size | Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| KN317757 | Tmem173 - mouse gene knockout kit via CRISPR, HDR mediated |
USD 1,657.00 |
|
| KN317757LP | Tmem173 - mouse gene knockout kit via CRISPR, HDR mediated |
USD 1,657.00 |
|
| KN317757RB | Tmem173 - mouse gene knockout kit via CRISPR, HDR mediated |
USD 1,657.00 |
|
| KN517757 | Tmem173 - KN2.0, Mouse gene knockout kit via CRISPR, non-homology mediated. |
USD 1,657.00 |
|
| GA209260 | Tmem173 CRISPRa kit - CRISPR gene activation of mouse transmembrane protein 173 |
USD 1,657.00 |
{0} Product Review(s)
Be the first one to submit a review






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China