ATP6V0E2 Rabbit Antibody
Frequently bought together (2)
beta Actin Mouse Monoclonal Antibody, Clone OTI1, Loading Control
USD 200.00
Transient overexpression lysate of ATPase, H+ transporting V0 subunit e2 (ATP6V0E2), transcript variant 2
USD 436.00
Other products for "ATP6V0E2"
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Reactivities | Human |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Immunogen | The immunogen for Anti-ATP6V0E2 Antibody is: synthetic peptide directed towards the N-terminal region of Human ATP6V0E2. Synthetic peptide located within the following region: GPWFVPKGPNRGVIITMLVATAVCCYLFWLIAILAQLNPLFGPQLKNETI |
| Formulation | Shipped as lyophilized powder. Purified antibody supplied in 1x PBS buffer with 0.09% (w/v) sodium azide and 2% sucrose. Note that this product is shipped as lyophilized powder to China customers. |
| Purification | Affinity Purified |
| Conjugation | Unconjugated |
| Storage | Store at -20°C as received. |
| Stability | Stable for 12 months from date of receipt. |
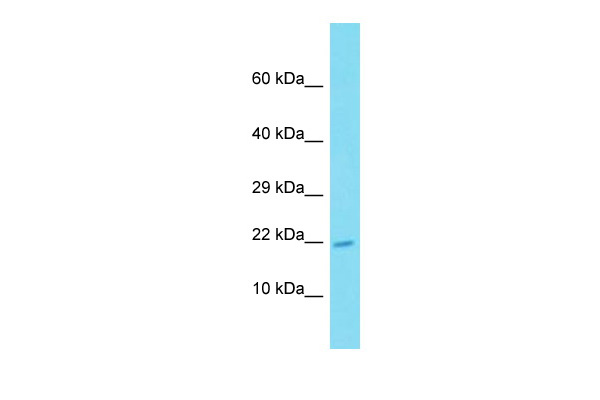
| Predicted Protein Size | 20 kDa |
| Database Link | |
| Background | Multisubunit vacuolar-type proton pumps, or H(+)-ATPases, acidify various intracellular compartments, such as vacuoles, clathrin-coated and synaptic vesicles, endosomes, lysosomes, and chromaffin granules. H(+)-ATPases are also found in plasma membranes of specialized cells, where they play roles in urinary acidification, bone resorption, and sperm maturation. Multiple subunits form H(+)-ATPases, with proteins of the V1 class hydrolyzing ATP for energy to transport H+, and proteins of the V0 class forming an integral membrane domain through which H+ is transported. ATP6V0E2 encodes an isoform of the H(+)-ATPase V0 e subunit, an essential proton pump component. |
| Synonyms | ATP6V0E2L; C7orf32 |
| Note | Immunogen sequence homology: Dog: 100%; Pig: 100%; Rat: 100%; Horse: 100%; Human: 100%; Mouse: 100%; Bovine: 100%; Rabbit: 100%; Guinea pig: 100%; Zebrafish: 93% |
| Reference Data | |
| Protein Pathways | Epithelial cell signaling in Helicobacter pylori infection, Metabolic pathways, Oxidative phosphorylation, Vibrio cholerae infection |
Documents
| Product Manuals |
| FAQs |
| SDS |
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China