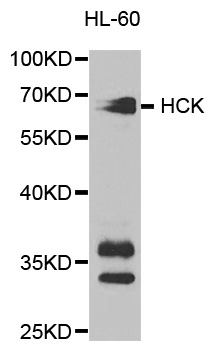
HCK Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
Frequently bought together (3)
beta Actin Mouse Monoclonal Antibody, Clone OTI1, Loading Control
USD 200.00
Transient overexpression lysate of hemopoietic cell kinase (HCK), transcript variant 2
USD 436.00
Other products for "HCK"
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Applications | ICC/IF, WB |
| Recommended Dilution | WB 1:500 - 1:2000;IF 1:10 - 1:100 |
| Reactivities | Human |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Immunogen | Recombinant protein of human HCK |
| Formulation | Store at -20C or -80C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3 |
| Concentration | lot specific |
| Purification | Affinity purification |
| Conjugation | Unconjugated |
| Storage | Store at -20°C as received. |
| Stability | Stable for 12 months from date of receipt. |
| Predicted Protein Size | 57 kDa |
| Gene Name | HCK proto-oncogene, Src family tyrosine kinase |
| Database Link | |
| Background | Hck (hemopoietic cell kinase) is a protein tyrosine kinase of the Src family prominently expressed in the lymphoid and myeloid lineages of hemopoiesis. It participates in transducing a variety of extracellular signals, which ultimately affect cellular processes including proliferation, differentiation and migration.The well-defined modular structure of Hck comprises a relatively divergent, NH2-terminal "unique" domain, which is subject to post-translational lipid modifications thereby targeting Hck to the plasma membrane. Src homology 3 (SH3) and 2 (SH2) domains, and a tyrosine kinase catalytic domain follow the "unique" domain. The catalytic activity of Hck is regulated, both positively and negatively, by tyrosine phosphorylation of highly conserved tyrosine (Y) residues. Phosphorylation of a single conserved Tyr499 residue in the COOH terminus of Hck by the protein kinase Csk renders Hck inactive as a result of an intramolecular interaction between the phosphorylated tyrosine (pY) residue and its own SH2 domain. Disruption of this interaction, either as a result of dephosphorylation, or substitution of the COOH-terminal regulatory Y residue with phenylalanine (F; e.g., HckY499F), or COOH-terminal truncation mutations as observed in the virally transduced v-Src oncoprotein, results in constitutive activation of Hck. In contrast to phosphorylation of the COOH-terminal regulatory tyrosine residue, autophosphorylation of a tyrosine residue (Tyr388) within the kinase domain of Hck acts to positively regulate its catalytic activity. Thus, activation of Hck requires both disruption of the COOH-terminal regulatory tyrosine-SH2 domain interaction and autophosphorylation of the regulatory tyrosine residue within the kinase domain. The dysfunction or dysregulation of Hck may contribute to the pathogenesis of some human leukemias. |
| Synonyms | JTK9 |
| Reference Data | |
| Protein Families | Druggable Genome, Protein Kinase |
| Protein Pathways | Chemokine signaling pathway, Fc gamma R-mediated phagocytosis |
Documents
| Product Manuals |
| FAQs |
| SDS |
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China