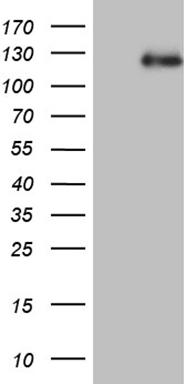
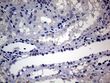
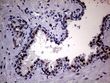
Androgen Receptor (AR) Mouse Monoclonal Antibody [Clone ID: OTI2E11]
CAT#: CF809203
Carrier-free (BSA/glycerol-free) AR mouse monoclonal antibody, clone OTI2E11
Formulation: Standard
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Clone Name | OTI2E11 |
| Applications | IHC, WB |
| Recommended Dilution | WB 1:2000, IHC 1:1000 |
| Reactivities | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host | Mouse |
| Isotype | IgG1 |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Immunogen | Human recombinant protein fragment corresponding to amino acids 420-659 of human AR(NP_000035) produced in E.coli. |
| Formulation | Lyophilized powder (original buffer 1X PBS, pH 7.3, 8% trehalose) |
| Reconstitution Method | For reconstitution, we recommend adding 100uL distilled water to a final antibody concentration of about 1 mg/mL. To use this carrier-free antibody for conjugation experiment, we strongly recommend performing another round of desalting process. (OriGene recommends Zeba Spin Desalting Columns, 7KMWCO from Thermo Scientific) |
| Purification | Purified from mouse ascites fluids or tissue culture supernatant by affinity chromatography (protein A/G) |
| Conjugation | Unconjugated |
| Storage | Store at -20°C as received. |
| Stability | Stable for 12 months from date of receipt. |
| Predicted Protein Size | 99 kDa |
| Gene Name | androgen receptor |
| Database Link | |
| Background | The androgen receptor gene is more than 90 kb long and codes for a protein that has 3 major functional domains: the N-terminal domain, DNA-binding domain, and androgen-binding domain. The protein functions as a steroid-hormone activated transcription factor. Upon binding the hormone ligand, the receptor dissociates from accessory proteins, translocates into the nucleus, dimerizes, and then stimulates transcription of androgen responsive genes. This gene contains 2 polymorphic trinucleotide repeat segments that encode polyglutamine and polyglycine tracts in the N-terminal transactivation domain of its protein. Expansion of the polyglutamine tract causes spinal bulbar muscular atrophy (Kennedy disease). Mutations in this gene are also associated with complete androgen insensitivity (CAIS). Two alternatively spliced variants encoding distinct isoforms have been described. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| Synonyms | AIS; AR8; DHTR; HUMARA; HYSP1; KD; NR3C4; SBMA; SMAX1; TFM |
| Reference Data | |
| Protein Families | Druggable Genome, Nuclear Hormone Receptor, Transcription Factors |
| Protein Pathways | Oocyte meiosis, Pathways in cancer, Prostate cancer |
Documents
| Product Manuals |
| FAQs |
| SDS |
Resources
| Antibody Resources |
Other Versions
| SKU | Description | Size | Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| TA809203 | AR mouse monoclonal antibody,clone OTI2E11 |
USD 447.00 |
|
| TA809203AM | AR mouse monoclonal antibody,clone OTI2E11, Biotinylated |
USD 509.00 |
|
| TA809203BM | AR mouse monoclonal antibody,clone OTI2E11, HRP conjugated |
USD 509.00 |
|
| TA809203S | AR mouse monoclonal antibody,clone OTI2E11 |
USD 200.00 |
{0} Product Review(s)
Be the first one to submit a review






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China