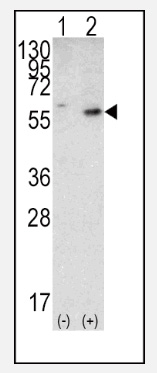
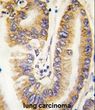
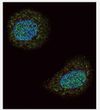
PTEN (N-term) Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
Other products for "PTEN"
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Applications | IF, IHC, WB |
| Recommended Dilution | Western blotting: 1/1000. Immunofluorescence: 1/10-1/50. Immunohistochemistry on Paraffin Sections: 1/50-1/100. |
| Reactivities | Human |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Isotype | Ig |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Immunogen | KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 69-104 amino acids from the N-terminal region of Human PTEN. |
| Specificity | This antibody recognizes Human PTEN at N-term. Other species not tested. |
| Formulation | PBS State: Purified State: Liquid purified Ig fraction Preservative: 0.09% (W/V) Sodium Azide |
| Concentration | lot specific |
| Purification | Protein G column, eluted with high and low pH buffers and neutralized immediately, followed by dialysis against PBS |
| Conjugation | Unconjugated |
| Storage | Store undiluted at 2-8°C for one month or (in aliquots) at -20°C for longer. Avoid repeated freezing and thawing. |
| Stability | Shelf life: one year from despatch. |
| Predicted Protein Size | 47166 Da |
| Gene Name | phosphatase and tensin homolog |
| Database Link | |
| Background | PTEN, (phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome 10), also known as MMAC1 (mutated in multiple advanced cancers 1), is a tumor suppressor implicated in a large number of human tumors. The PTEN phosphatase incorporates the catalytic motif (HCXXGXXRS/T) that is a signature of the protein tyrosine phosphatase family. Recombinant human PTEN is a dual phosphatase with ability to dephosphorylate both tyrosine and serine/threonine residues. PTEN functions primarily as a lipid phosphatase to regulate signal transduction pathways, with a primary target identified as phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5 trisphosphate. In addition, PTEN presents weak tyrosine phosphatase activity, which may downregulate signaling pathways involving focal adhesion kinase or Shc. PTEN negatively regulates activation of the serine/threonine kinase Akt/PKB by blocking its phosphorylation, thereby inhibiting the PI 3 kinase Akt signaling pathway, which is important for cell survival. In vivo, the majority of PTEN missense mutations detected in tumor specimens target the phosphatase domain and cause a loss in PTEN phosphatase activity. Mutations in PTEN are associated with several common cancers including prostate, brain and breast cancer, and with Cowden's disease, an autosomal dominant disorder conferring susceptibility to benign and malignant tumors. Germline mutations of PTEN are also linked Lhermitte-Duclos disease and Bannayan-Zonana syndrome. Mutations of PTEN occur in 60 to 80% of prostate cancers. PTEN is also essential for embryonic development. |
| Synonyms | MMAC1, TEP1 |
| Reference Data | |
Documents
| Product Manuals |
| FAQs |
| SDS |
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China