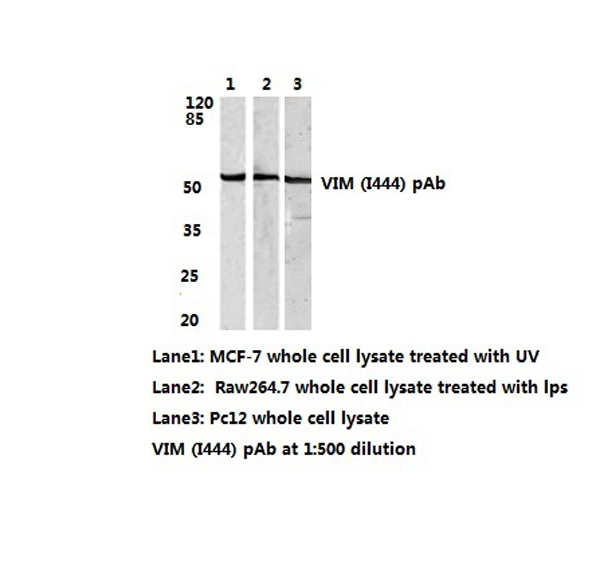
Vimentin (VIM) Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
Other products for "VIM"
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Applications | IF, IHC, WB |
| Recommended Dilution | Western Blot: 1/500-1/1000. Immunofluorescence: 1/50-1/200. Immunohistochemistry on Paraffin Sections: 1/50-1/200. |
| Reactivities | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide, corresponding to amino acids 411-460 of Human Vimentin. |
| Specificity | This antibody detects endogenous levels of Vimentin protein. (region surrounding Ile444) |
| Formulation | Phosphate buffered saline (PBS), pH~7.2 State: Aff - Purified State: Liquid purified Ig fraction (>95% pure by SDS-PAGE) Preservative: 15 mM Sodium Azide |
| Concentration | 1.0 mg/ml |
| Purification | Affinity Chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen |
| Conjugation | Unconjugated |
| Storage | Store undiluted at 2-8°C for one month or (in aliquots) at -20°C for longer. Avoid repeated freezing and thawing. |
| Stability | Shelf life: one year from despatch. |
| Predicted Protein Size | ~48.0 kDa |
| Gene Name | vimentin |
| Database Link | |
| Background | Xeroderma pigmentosum (XP) is an autosomal recessive disorder characterized by a genetic predisposition to sunlight-induced skin cancer due to deficiencies in the DNA repair enzymes. The most frequent mutations are found in the XP genes of group A through G and group V, which encode nucleotide excision repair proteins. Nucleotide excision repair (NER) is the normal cellular response to DNA damage induced by UV irradiation and is disrupted in patients with XP. Xeroderma pigmentosum group A (XPA) is an essential NER factor that coordinates the collection of a preincision complex during the processing of DNA damage. XPA may also have a role in the repair of oxidized DNA bases. XPA is sensitive not only to the structure of the DNA double helix, but also to bulky groups incorporated into DNA. XPA forms a homodimer in the absence of DNA, but binds to DNA in both monomeric and dimeric forms. The dimerically bound XPA is much more efficient, so cells probably regulate XPA activity in a concentration-dependent manner. XPA deficient organisms cannot repair UV-induced DNA damage and thus acquire skin cancers by UV irradiation very easily. |
| Synonyms | VIM |
| Reference Data | |
Documents
| Product Manuals |
| FAQs |
| SDS |
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China