WNT4 (NM_030761) Human Recombinant Protein
CAT#: TP761294
Purified recombinant protein of Human wingless-type MMTV integration site family, member 4 (WNT4), full length, with N-terminal GST and C-terminal His tag, expressed in E. coli, 50ug
Frequently bought together (1)
Other products for "WNT4"
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Species | Human |
| Expression Host | E. coli |
| Expression cDNA Clone or AA Sequence |
A DNA sequence encoding human full-length WNT4
|
| Tag | N-GST and C-His |
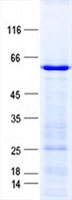
| Predicted MW | 64.6 kDa |
| Concentration | >0.05 µg/µL as determined by microplate BCA method |
| Purity | > 80% as determined by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie blue staining |
| Buffer | 25 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.0, 150 mM NaCl, 1% sarkosyl, 10% glycerol |
| Note | For testing in cell culture applications, please filter before use. Note that you may experience some loss of protein during the filtration process. |
| Storage | Store at -80°C. |
| Stability | Stable for 12 months from the date of receipt of the product under proper storage and handling conditions. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Reference Data | |
| RefSeq | NP_110388 |
| Locus ID | 54361 |
| UniProt ID | P56705 |
| Cytogenetics | 1p36.12 |
| Refseq Size | 3905 |
| Refseq ORF | 1053 |
| Synonyms | SERKAL; WNT-4 |
| Summary | The WNT gene family consists of structurally related genes which encode secreted signaling proteins. These proteins have been implicated in oncogenesis and in several developmental processes, including regulation of cell fate and patterning during embryogenesis. This gene is a member of the WNT gene family, and is the first signaling molecule shown to influence the sex-determination cascade. It encodes a protein which shows 98% amino acid identity to the Wnt4 protein of mouse and rat. This gene and a nuclear receptor known to antagonize the testis-determining factor play a concerted role in both the control of female development and the prevention of testes formation. This gene and another two family members, WNT2 and WNT7B, may be associated with abnormal proliferation in breast tissue. Mutations in this gene can result in Rokitansky-Kuster-Hauser syndrome and in SERKAL syndrome. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| Protein Families | Druggable Genome, Secreted Protein, Transmembrane |
| Protein Pathways | Basal cell carcinoma, Hedgehog signaling pathway, Melanogenesis, Pathways in cancer, Wnt signaling pathway |
Documents
| FAQs |
| SDS |
Resources
Recombinant Protein Resources |
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China