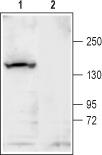
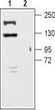
Kcnt1 Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
Frequently bought together (1)
beta Actin Mouse Monoclonal Antibody, Clone OTI1, Loading Control
USD 200.00
Other products for "Kcnt1"
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Applications | WB |
| Recommended Dilution | WB: 1:200-1:2000 |
| Reactivities | Mouse, Rat |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Immunogen | Peptide (C)KQEEKQNRRGLAG, corresponding to amino acid residues 619-631 of rat Slack . Intracellular, C-terminal. |
| Formulation | Lyophilized. Concentration before lyophilization ~0.8mg/ml (lot dependent, please refer to CoA along with shipment for actual concentration). Buffer before lyophilization: Phosphate buffered saline (PBS), pH 7.4, 1% BSA, 0.025% NaN3. |
| Reconstitution Method | Add 50 ul double distilled water (DDW) to the lyophilized powder. |
| Purification | Affinity purified on immobilized antigen. |
| Conjugation | Unconjugated |
| Storage | Store at -20°C as received. |
| Stability | Stable for 12 months from date of receipt. |
| Gene Name | potassium sodium-activated channel subfamily T member 1 |
| Database Link | |
| Background | KCa4.1 (Na+ activated K+ channel, Slack, Slo2.2, KCNT1) is a member of a subgroup within the Ca2+ activated K+ channel family. The Slack (sequence like a Ca2+-activated K+ channel) and Slick (sequence like an intermediate conductance K+ channel, KCNT2) genes, which encode Na+-activated K+ (KNa) channels, are expressed at high levels in neurons in several areas of the nervous system.Although KCa4.1 is functionally a Na+ activated K+ channel, it is termed KCa by the IUPHAR nomenclature, due to its sequence homology to other KCa channels.The familyâ??s protein topology consists of six transmembrane domains that flank a single and highly conserved pore region with intracellular N- and C-termini. As is the case for the voltage-dependent K+ channels the functional unit for KCa4.1 channels is composed of four subunits that can assemble as either homo or heteromers with KCNT2 (Slick). KCa4.1 and Slick subunits coassemble to form heteromeric channels that differ from the homomers in their unitary conductance, kinetic behavior, subcellular localization, and response to activation of protein kinase C. Heteromer formation requires the N-terminal domain of Slack-B, one of the alternative splice variants of the KCa4.1 channel. This cytoplasmic N-terminal domain of Slack-B also facilitates the localization of heteromeric KNa channels to the plasma membrane. K+ channels sensitive to intracellular Na+, termed KNa channels, shape neuronal excitability. KNa channels contribute to the adaptation of firing rates and to slow after-hyperpolarizations that follow repetitive firing. In certain neurons, they also appear to be activated by Na+ influx accompanying single action potentials. Their molecular properties also suggest that these channels contribute to the response of neurons to hypoxia1. KCa4.1 channels were shown to be expressed also in dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neurons, where these channels were found to contain a NAD+ binding sequence and to be modulated by this endogenous compound3. |
| Synonyms | bA100C15.2; FLJ41282; KCa4.1; KIAA1422; SLACK |
| Reference Data | |
Documents
| Product Manuals |
| FAQs |
| SDS |
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China