PLGF (PGF) Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
Other products for "PGF"
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Applications | ELISA, WB |
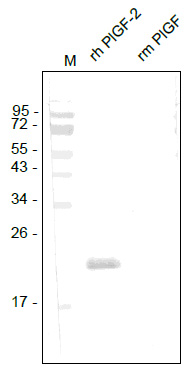
| Recommended Dilution | Western Blot: 2-6 µg/ml, it will detect 25-50 ng/lane of recombinant Human PlGF-1 and PlGF-2 under reducing and non-reducing conditions. ELISA: 1-5 µg/ml, allows the detection of 1.0-2.5 ng/well of recombinant Human PlGF-1 and PlGF-2. |
| Reactivities | Human |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Immunogen | Highly pure recombinant Human PlGF-2 [Leu19 – Arg170] produced in insect cells. |
| Specificity | The antibody will react with all Human PlGF isoforms. |
| Formulation | PBS, pH 7.4 containing no preservative State: Purified State: Lyophilized purified Ig fraction |
| Reconstitution Method | Restore in sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/ml. |
| Purification | Affinity Chromatography on Protein A |
| Conjugation | Unconjugated |
| Storage | Store lyophilized at 2-8°C for 6 months or at -20°C long term. After reconstitution store the antibody undiluted at 2-8°C for one month or (in aliquots) at -20°C long term. Avoid repeated freezing and thawing. |
| Stability | Shelf life: one year from despatch. |
| Database Link | |
| Background | Placenta growth factor (PlGF) is a member of the PDGF/VEGF family of growth factors that share a conserved pattern of eight cysteines. Alternate splicing results in at least three human mature PlGF forms containing 131 (PlGF1), 152 (PlGF2), and 203 (PlGF3) amino acids (aa) respectively. Only PlGF2 contains a highly basic heparinbinding 21 aa insert at the C-terminus. In the mouse, only one P lGF that is the equivalent of human PlGF2 has been identified. Human PlGF1 shares 56%, 55%, 74% and 95% aa identity with the appropriate isoform of mouse, rat, canine and equine PlGF. PlGF is mainly found as variably glycosylated, secreted, 55 - 60 kDa disulfide linked homodimers. Mammalian cells expressing PlGF include villous trophoblasts, decidual cells, erythroblasts, keratinocytes and some endothelial cells. Circulating PlGF increases during pregnancy, reaching a peak in mid-gestation; this increase is attenuated in preeclampsia. However, deletion of PlGF in the mouse does not affect development or reproduction. Postnatally, mice lacking PlGF show impaired angiogenesis in response to ischemia. PlGF binds and signals through VEGF R1/Flt1, but not VEGF R2/Flk-1/KDR, while VEGF binds both but signals only through the angiogenic receptor, VEGF R2. PlGF and VEGF therefore compete for binding to VEGF R1, allowing high PlGF to discourage VEGF/VEGF R1 binding and promote VEGF/VEGF R2mediated angiogenesis. However, PlGF (especially PlGF1) and some forms of VEGF can form dimers that decrease the angiogenic effect of VEGF on VEGF R2. PlGF2, but not PLGF-1, shows heparindependent binding of neuropilin (Npn)-1 and Npn2. PlGF induces monocyte activation, migration, and production of inflammatory cytokines and VEGF. These activities facilitate wound and bone fracture healing, but also contribute to inflammation in active sickle cell disease and atherosclerosis. |
| Synonyms | PGFL, PLGF, PlGF |
| Reference Data | |
Documents
| Product Manuals |
| FAQs |
| SDS |
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China